Week 3 [Aug 27]
Todo
Admin info to read:
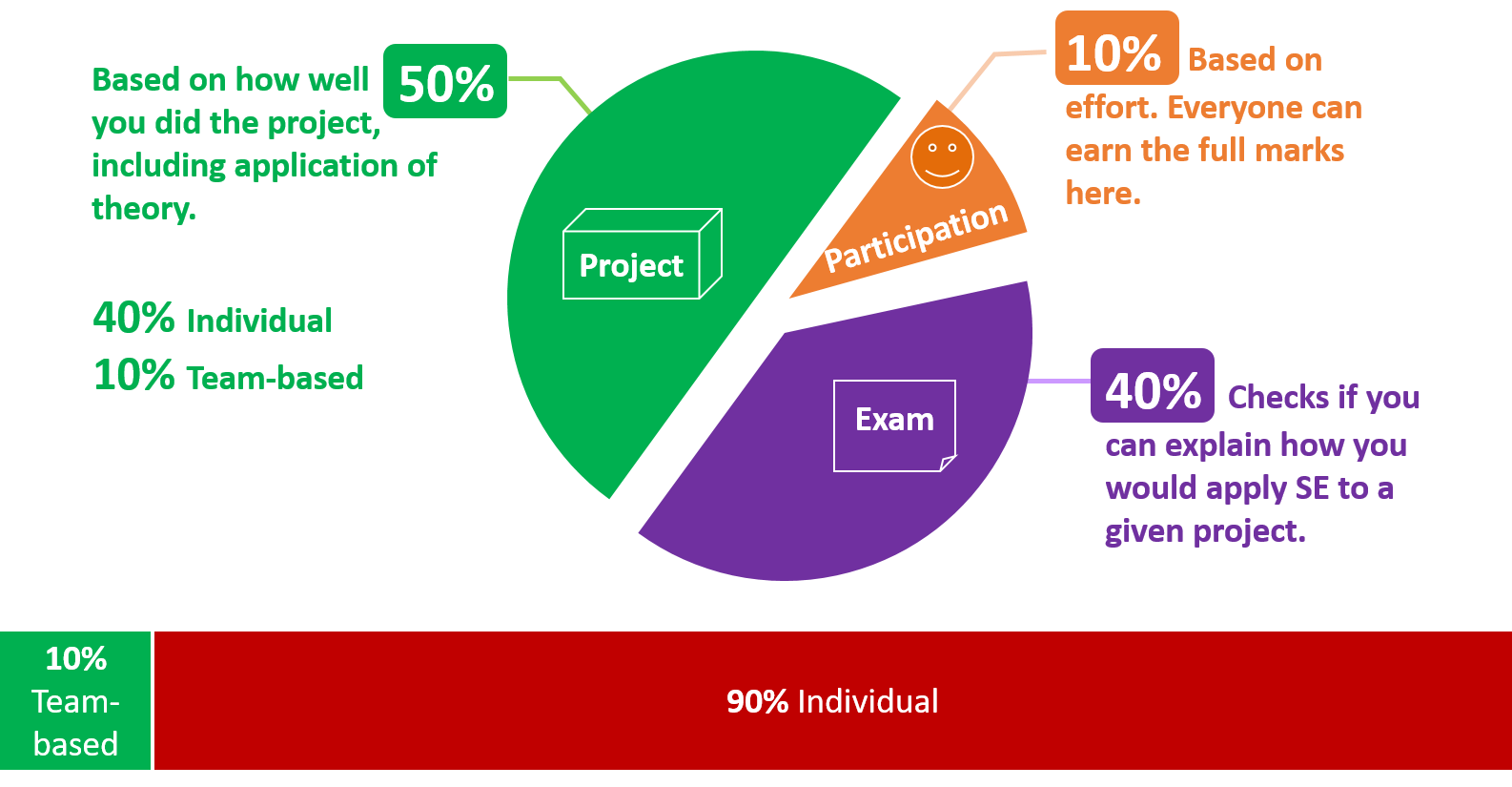
Note that project grading is not competitive (not bell curved). CS2113T projects will be assessed separately from CS2113 projects. This is to account for the perceived difference in workload. Given below is the marking scheme.
Total: 50 marks ( 40 individual marks + 10 team marks)
Evaluates: How well do your features fit together to form a cohesive product (not how many features or how big the features are)?
Based on: user guide and the product demo. The quality of the demo will be factored in as well.
❗️ Feature that fits well with the other features will earn more marks.
Evaluates:
A. Code quality/quantity:
How good your implementation is, in terms of the quality and the quantity of the code you have written yourself.
Based on: an inspection of the collated code (obtained from Reposense).
-
Ensure your code has at least some evidence of these (see here for more info)
- logging
- exceptions
- assertions
- defensive coding
-
Ensure there are no coding standard violations e.g. all boolean variables/methods sounds like booleans. Checkstyle can prevent only some coding standard violations; others need to be checked manually.
-
Ensure SLAP is applied at a reasonable level. Long methods or deeply-nested code are symptoms of low-SLAP may be counted against your code quality.
-
Reduce code duplications i.e. if there multiple blocks of code that vary only in minor ways, try to extract out similarities into one place, especially in test code.
-
In addition, try to apply as many of the
code quality guidelines covered in the module as much as you can.
Code Quality
Introduction
Basic
Can explain the importance of code quality
Always code as if the person who ends up maintaining your code will be a violent psychopath who knows where you live. -- Martin Golding
Guideline: Maximise Readability
Introduction
Can explain the importance of readability
Programs should be written and polished until they acquire publication quality. --Niklaus Wirth
Among various dimensions of code quality, such as run-time efficiency, security, and robustness, one of the most important is understandability. This is because in any non-trivial software project, code needs to be read, understood, and modified by other developers later on. Even if we do not intend to pass the code to someone else, code quality is still important because we all become 'strangers' to our own code someday.
The two code samples given below achieve the same functionality, but one is easier to read.
|
Bad |
|
Good |
|
Bad |
|
Good |
Basic
Avoid Long Methods
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid long methods
Be wary when a method is longer than the computer screen, and take corrective action when it goes beyond 30 LOC (lines of code). The bigger the haystack, the harder it is to find a needle.
Avoid Deep Nesting
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid deep nesting
If you need more than 3 levels of indentation, you're screwed anyway, and should fix your program. --Linux 1.3.53 CodingStyle
In particular, avoid arrowhead style code.
Example:
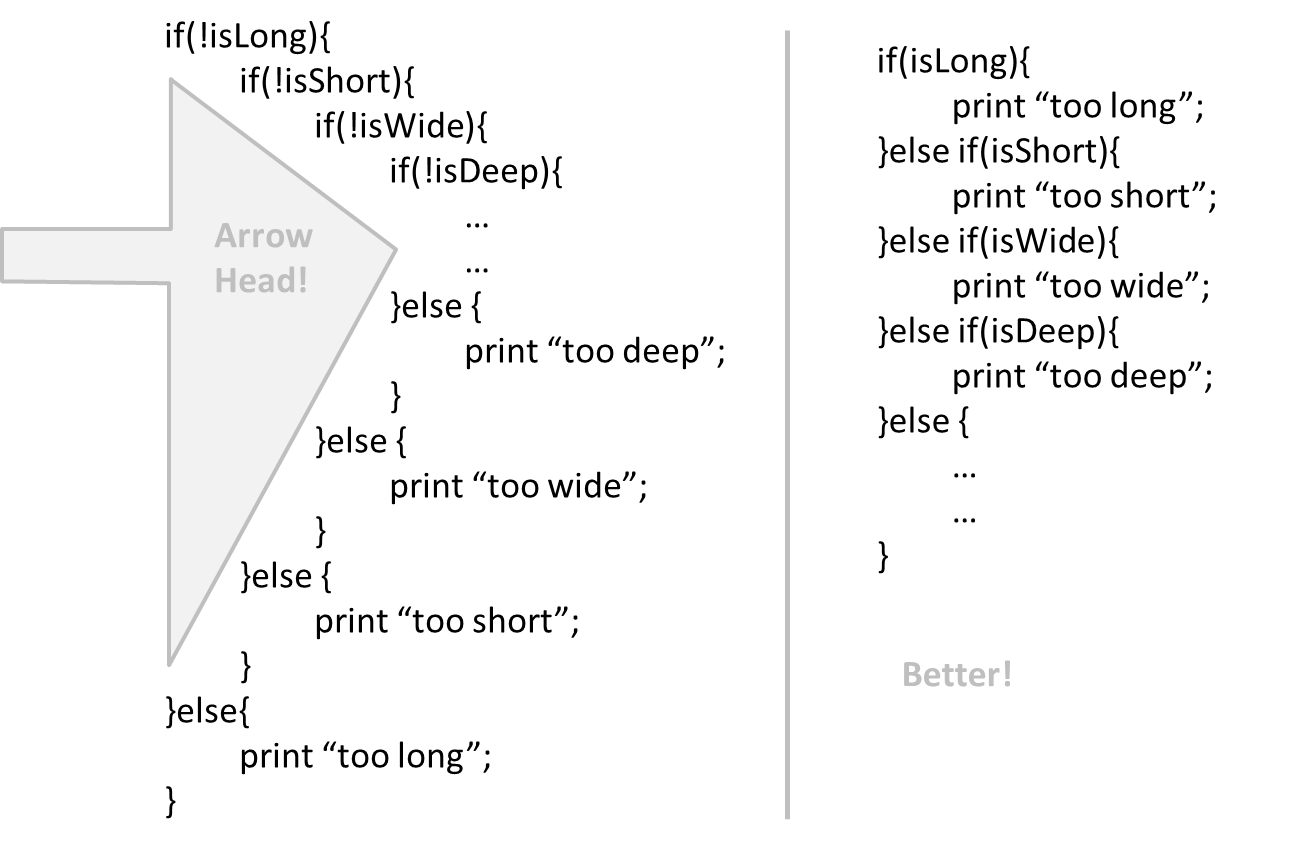
Avoid Complicated Expressions
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid complicated expressions
Avoid complicated expressions, especially those having many negations and nested parentheses. If you must evaluate complicated expressions, have it done in steps (i.e. calculate some intermediate values first and use them to calculate the final value).
Example:
Bad
return ((length < MAX_LENGTH) || (previousSize != length)) && (typeCode == URGENT);
Good
boolean isWithinSizeLimit = length < MAX_LENGTH;
boolean isSameSize = previousSize != length;
boolean isValidCode = isWithinSizeLimit || isSameSize;
boolean isUrgent = typeCode == URGENT;
return isValidCode && isUrgent;
Example:
Bad
return ((length < MAX_LENGTH) or (previous_size != length)) and (type_code == URGENT)
Good
is_within_size_limit = length < MAX_LENGTH
is_same_size = previous_size != length
is_valid_code = is_within_size_limit or is_same_size
is_urgent = type_code == URGENT
return is_valid_code and is_urgent
The competent programmer is fully aware of the strictly limited size of his own skull; therefore he approaches the programming task in full humility, and among other things he avoids clever tricks like the plague. -- Edsger Dijkstra
Avoid Magic Numbers
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid magic numbers
When the code has a number that does not explain the meaning of the number, we call that a magic number (as in “the number appears as if by magic”). Using a
Example:
|
Bad |
|
Good |
Note: Python does not have a way to make a variable a constant. However, you can use a normal variable with an ALL_CAPS name to simulate a constant.
|
Bad |
|
Good |
Similarly, we can have ‘magic’ values of other data types.
Bad
"Error 1432" // A magic string!
Make the Code Obvious
Can improve code quality using technique: make the code obvious
Make the code as explicit as possible, even if the language syntax allows them to be implicit. Here are some examples:
- [
Java] Use explicit type conversion instead of implicit type conversion. - [
Java,Python] Use parentheses/braces to show grouping even when they can be skipped. - [
Java,Python] Useenumerations when a certain variable can take only a small number of finite values. For example, instead of declaring the variable 'state' as an integer and using values 0,1,2 to denote the states 'starting', 'enabled', and 'disabled' respectively, declare 'state' as typeSystemStateand define an enumerationSystemStatethat has values'STARTING','ENABLED', and'DISABLED'.
Intermediate
Structure Code Logically
Can improve code quality using technique: structure code logically
Lay out the code so that it adheres to the logical structure. The code should read like a story. Just like we use section breaks, chapters and paragraphs to organize a story, use classes, methods, indentation and line spacing in your code to group related segments of the code. For example, you can use blank lines to group related statements together. Sometimes, the correctness of your code does not depend on the order in which you perform certain intermediary steps. Nevertheless, this order may affect the clarity of the story you are trying to tell. Choose the order that makes the story most readable.
Do Not 'Trip Up' Reader
Can improve code quality using technique: do not 'trip up' reader
Avoid things that would make the reader go ‘huh?’, such as,
- unused parameters in the method signature
- similar things look different
- different things that look similar
- multiple statements in the same line
- data flow anomalies such as, pre-assigning values to variables and modifying it without any use of the pre-assigned value
Practice KISSing
Can improve code quality using technique: practice kissing
As the old adage goes, "keep it simple, stupid” (KISS). Do not try to write ‘clever’ code. For example, do not dismiss the brute-force yet simple solution in favor of a complicated one because of some ‘supposed benefits’ such as 'better reusability' unless you have a strong justification.
Debugging is twice as hard as writing the code in the first place. Therefore, if you write the code as cleverly as possible, you are, by definition, not smart enough to debug it. --Brian W. Kernighan
Programs must be written for people to read, and only incidentally for machines to execute. --Abelson and Sussman
Avoid Premature Optimizations
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid premature optimizations
Optimizing code prematurely has several drawbacks:
- We may not know which parts are the real performance bottlenecks. This is especially the case when the code undergoes transformations (e.g. compiling, minifying, transpiling, etc.) before it becomes an executable. Ideally, you should use a profiler tool to identify the actual bottlenecks of the code first, and optimize only those parts.
- Optimizing can complicate the code, affecting correctness and understandability
- Hand-optimized code can be harder for the compiler to optimize (the simpler the code, the easier for the compiler to optimize it). In many cases a compiler can do a better job of optimizing the runtime code if you don't get in the way by trying to hand-optimize the source code.
A popular saying in the industry is make it work, make it right, make it fast which means in most cases getting the code to perform correctly should take priority over optimizing it. If the code doesn't work correctly, it has no value on matter how fast/efficient it it.
Premature optimization is the root of all evil in programming. --Donald Knuth
Note that there are cases where optimizing takes priority over other things e.g. when writing code for resource-constrained environments. This guideline simply a caution that you should optimize only when it is really needed.
SLAP Hard
Can improve code quality using technique: SLAP hard
Avoid varying the level of
Example:
Bad
readData();
salary = basic*rise+1000;
tax = (taxable?salary*0.07:0);
displayResult();
Good
readData();
processData();
displayResult();
Design → Design Fundamentals → Abstraction →
What
Abstraction is a technique for dealing with complexity. It works by establishing a level of complexity (or an aspect) we are interested in, and suppressing the more complex details below that level (or irrelevant to that aspect).
Most programs are written to solve complex problems involving large amounts of intricate details. It is impossible to deal with all these details at the same time. The guiding principle of abstraction stipulates that we capture only details that are relevant to the current perspective or the task at hand.
Ignoring lower level data items and thinking in terms of bigger entities is called data abstraction.
Within a certain software component, we might deal with a user data type, while ignoring the details contained in the user data item such as name, and date of birth. These details have been ‘abstracted away’ as they do not affect the task of that software component.
Control abstraction abstracts away details of the actual control flow to focus on tasks at a simplified level.
print(“Hello”) is an abstraction of the actual output mechanism within the computer.
Abstraction can be applied repeatedly to obtain progressively higher levels of abstractions.
An example of different levels of data abstraction: a File is a data item that is at a higher level than an array and an array is at a higher level
than a bit.
An example of different levels of control abstraction: execute(Game) is at a higher level than print(Char) which is at a higher than
an Assembly language instruction MOV.
Advanced
Make the Happy Path Prominent
Can improve code quality using technique: make the happy path prominent
The happy path (i.e. the execution path taken when everything goes well) should be clear and prominent in your code. Restructure the code to make the happy path unindented as much as possible. It is the ‘unusual’ cases that should be indented. Someone reading the code should not get distracted by alternative paths taken when error conditions happen. One technique that could help in this regard is the use of guard clauses.
Example:
Bad
if (!isUnusualCase) { //detecting an unusual condition
if (!isErrorCase) {
start(); //main path
process();
cleanup();
exit();
} else {
handleError();
}
} else {
handleUnusualCase(); //handling that unusual condition
}
In the code above,
- Unusual condition detection is separated from their handling.
- Main path is nested deeply.
Good
if (isUnusualCase) { //Guard Clause
handleUnusualCase();
return;
}
if (isErrorCase) { //Guard Clause
handleError();
return;
}
start();
process();
cleanup();
exit();
In contrast, the above code
- deals with unusual conditions as soon as they are detected so that the reader doesn't have to remember them for long.
- keeps the main path un-indented.
Guideline: Follow a Standard
Introduction
Can explain the need for following a standard
One essential way to improve code quality is to follow a consistent style. That is why software engineers follow a strict coding standard (aka style guide).
The aim of a coding standard is to make the entire code base look like it was written by one person. A coding standard is usually specific to a programming language and specifies guidelines such as the location of opening and closing braces, indentation styles and naming styles (e.g. whether to use Hungarian style, Pascal casing, Camel casing, etc.). It is important that the whole team/company use the same coding standard and that standard is not generally inconsistent with typical industry practices. If a company's coding standards is very different from what is used typically in the industry, new recruits will take longer to get used to the company's coding style.
💡 IDEs can help to enforce some parts of a coding standard e.g. indentation rules.
What is the recommended approach regarding coding standards?
c
What is the aim of using a coding standard? How does it help?
Basic
Can follow simple mechanical style rules
Learn basic guidelines of the Java coding standard (by OSS-Generic)
Sample coding standard: PEP 8 Python Style Guide -- by Python.org
Consider the code given below:
import java.util.*;
public class Task {
public static final String descriptionPrefix = "description: ";
private String description;
private boolean important;
List<String> pastDescription = new ArrayList<>(); // a list of past descriptions
public Task(String d) {
this.description = d;
if (!d.isEmpty())
this.important = true;
}
public String getAsXML() { return "<task>"+description+"</task>"; }
/**
* Print the description as a string.
*/
public void printingDescription(){ System.out.println(this); }
@Override
public String toString() { return descriptionPrefix + description; }
}
In what ways the code violate the basic guidelines (i.e., those marked with one ⭐️) of the OSS-Generic Java Coding Standard given here?
Here are three:
descriptionPrefixis a constant and should be namedDESCRIPTION_PREFIX- method name
printingDescription()should be named asprintDescription() - boolean variable
importantshould be named to sound boolean e.g.,isImportant
There are many more.
Intermediate
Can follow intermediate style rules
Go through the provided Java coding standard and learn the intermediate style rules.
According to the given Java coding standard, which one of these is not a good name?
b
Explanation: checkWeight is an action. Naming variables as actions makes the code harder to follow. isWeightValid may be a better name.
Repeat the exercise in the panel below but also find violations of intermediate level guidelines.
Consider the code given below:
import java.util.*;
public class Task {
public static final String descriptionPrefix = "description: ";
private String description;
private boolean important;
List<String> pastDescription = new ArrayList<>(); // a list of past descriptions
public Task(String d) {
this.description = d;
if (!d.isEmpty())
this.important = true;
}
public String getAsXML() { return "<task>"+description+"</task>"; }
/**
* Print the description as a string.
*/
public void printingDescription(){ System.out.println(this); }
@Override
public String toString() { return descriptionPrefix + description; }
}
In what ways the code violate the basic guidelines (i.e., those marked with one ⭐️) of the OSS-Generic Java Coding Standard given here?
Here are three:
descriptionPrefixis a constant and should be namedDESCRIPTION_PREFIX- method name
printingDescription()should be named asprintDescription() - boolean variable
importantshould be named to sound boolean e.g.,isImportant
There are many more.
Here's one you are more likely to miss:
* Print the description as a string.→* Prints the description as a string.
There are more.
Guideline: Name Well
Introduction
Can explain the need for good names in code
Proper naming improves the readability. It also reduces bugs caused by ambiguities regarding the intent of a variable or a method.
There are only two hard things in Computer Science: cache invalidation and naming things. -- Phil Karlton
Basic
Use Nouns for Things and Verbs for Actions
Can improve code quality using technique: use nouns for things and verbs for actions
Use nouns for classes/variables and verbs for methods/functions.
Examples:
| Name for a | Bad | Good |
|---|---|---|
| Class | CheckLimit |
LimitChecker |
| method | result() |
calculate() |
Distinguish clearly between single-valued and multivalued variables.
Examples:
Good
Person student;
ArrayList<Person> students;
Good
student = Person('Jim')
students = [Person('Jim'), Person('Alice')]
Use Standard Words
Can improve code quality using technique: use standard words
Use correct spelling in names. Avoid 'texting-style' spelling. Avoid foreign language words, slang, and names that are only meaningful within specific contexts/times e.g. terms from private jokes, a TV show currently popular in your country
Intermediate
Use Name to Explain
Can improve code quality using technique: use name to explain
A name is not just for differentiation; it should explain the named entity to the reader accurately and at a sufficient level of detail.
Examples:
| Bad | Good |
|---|---|
processInput() (what 'process'?) |
removeWhiteSpaceFromInput() |
flag |
isValidInput |
temp |
If the name has multiple words, they should be in a sensible order.
Examples:
| Bad | Good |
|---|---|
bySizeOrder() |
orderBySize() |
Imagine going to the doctor's and saying "My eye1 is swollen"! Don’t use numbers or case to distinguish names.
Examples:
| Bad | Bad | Good |
|---|---|---|
value1, value2 |
value, Value |
originalValue, finalValue |
Not Too Long, Not Too Short
Can improve code quality using technique: not too long, not too short
While it is preferable not to have lengthy names, names that are 'too short' are even worse. If you must abbreviate or use acronyms, do it consistently. Explain their full meaning at an obvious location.
Avoid Misleading Names
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid misleading names
Related things should be named similarly, while unrelated things should NOT.
Example: Consider these variables
colorBlack: hex value for color blackcolorWhite: hex value for color whitecolorBlue: number of times blue is usedhexForRed: : hex value for color red
This is misleading because colorBlue is named similar to colorWhite and colorBlack but has a different purpose while hexForRed is named differently but
has very similar purpose to the first two variables. The following is better:
hexForBlackhexForWhitehexForRedblueColorCount
Avoid misleading or ambiguous names (e.g. those with multiple meanings), similar sounding names, hard-to-pronounce ones (e.g. avoid ambiguities like "is that a lowercase L, capital I or number 1?", or "is that number 0 or letter O?"), almost similar names.
Examples:
| Bad | Good | Reason |
|---|---|---|
phase0 |
phaseZero |
Is that zero or letter O? |
rwrLgtDirn |
rowerLegitDirection |
Hard to pronounce |
right left wrong |
rightDirection leftDirection wrongResponse |
right is for 'correct' or 'opposite of 'left'? |
redBooks readBooks |
redColorBooks booksRead |
red and read (past tense) sounds the same |
FiletMignon |
egg |
If the requirement is just a name of a food, egg is a much easier to type/say choice than FiletMignon |
Guideline: Avoid Unsafe Shortcuts
Introduction
Can explain the need for avoiding error-prone shortcuts
It is safer to use language constructs in the way they are meant to be used, even if the language allows shortcuts. Some such coding practices are common sources of bugs. Know them and avoid them.
Basic
Use the Default Branch
Can improve code quality using technique: use the default branch
Always include a default branch in case statements.
Furthermore, use it for the intended default action and not just to execute the last option. If there is no default action, you can use the 'default' branch to detect errors (i.e. if execution reached the
default branch, throw an exception). This also applies to the final else of an if-else construct. That is, the final else should mean 'everything else',
and not the final option. Do not use else when an if condition can be explicitly specified, unless there is absolutely no other possibility.
Bad
if (red) print "red";
else print "blue";
Good
if (red) print "red";
else if (blue) print "blue";
else error("incorrect input");
Don't Recycle Variables or Parameters
Can improve code quality using technique: don't recycle variables or parameters
- Use one variable for one purpose. Do not reuse a variable for a different purpose other than its intended one, just because the data type is the same.
- Do not reuse formal parameters as local variables inside the method.
Bad
double computeRectangleArea(double length, double width) {
length = length * width;
return length;
}
Good
double computeRectangleArea(double length, double width) {
double area;
area = length * width;
return area;
}
Avoid Empty Catch Blocks
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid empty catch blocks
Never write an empty catch statement. At least give a comment to explain why the catch block is left empty.
Delete Dead Code
Can improve code quality using technique: delete dead code
We all feel reluctant to delete code we have painstakingly written, even if we have no use for that code any more ("I spent a lot of time writing that code; what if we need it again?"). Consider all code as baggage you have to carry; get rid of unused code the moment it becomes redundant. If you need that code again, simply recover it from the revision control tool you are using. Deleting code you wrote previously is a sign that you are improving.
Intermediate
Minimise Scope of Variables
Can improve code quality using technique: minimise scope of variables
Minimize global variables. Global variables may be the most convenient way to pass information around, but they do create implicit links between code segments that use the global variable. Avoid them as much as possible.
Define variables in the least possible scope. For example, if the variable is used only within the if block of the conditional statement, it should be declared inside that if block.
The most powerful technique for minimizing the scope of a local variable is to declare it where it is first used. -- Effective Java, by Joshua Bloch
Resources:
Minimise Code Duplication
Can improve code quality using technique: minimise code duplication
Code duplication, especially when you copy-paste-modify code, often indicates a poor quality implementation. While it may not be possible to have zero duplication, always think twice before duplicating code; most often there is a better alternative.
This guideline is closely related to the
Supplmentary → Principles →
DRY Principle
DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) Principle: Every piece of knowledge must have a single, unambiguous, authoritative representation within a system The Pragmatic Programmer, by Andy Hunt and Dave Thomas
This principle guards against duplication of information.
The functionality implemented twice is a violation of the DRY principle even if the two implementations are different.
The value a system-wide timeout being defined in multiple places is a violation of DRY.
Guideline: Comment Minimally, but Sufficiently
Introduction
Can explain the need for commenting minimally but sufficiently
Good code is its own best documentation. As you’re about to add a comment, ask yourself, ‘How can I improve the code so that this comment isn’t needed?’ Improve the code and then document it to make it even clearer. --Steve McConnell, Author of Clean Code
Some think commenting heavily increases the 'code quality'. This is not so. Avoid writing comments to explain bad code. Improve the code to make it self-explanatory.
Basic
Do Not Repeat the Obvious
Can improve code quality using technique: do not repeat the obvious
If the code is self-explanatory, refrain from repeating the description in a comment just for the sake of 'good documentation'.
Bad
// increment x
x++;
//trim the input
trimInput();
Write to the Reader
Can improve code quality using technique: write to the reader
Do not write comments as if they are private notes to self. Instead, write them well enough to be understood by another programmer. One type of comments that is almost always useful is the header comment that you write for a class or an operation to explain its purpose.
Examples:
Bad Reason: this comment will only make sense to the person who wrote it
// a quick trim function used to fix bug I detected overnight
void trimInput(){
....
}
Good
/** Trims the input of leading and trailing spaces */
void trimInput(){
....
}
Bad Reason: this comment will only make sense to the person who wrote it
# a quick trim function used to fix bug I detected overnight
def trim_input():
...
Good
def trim_input():
"""Trim the input of leading and trailing spaces"""
...
Intermediate
Explain WHAT and WHY, not HOW
Can improve code quality using technique: explain what and why, not how
Comments should explain what and why aspect of the code, rather than the how aspect.
👍 What : The specification of what the code supposed to do. The reader can compare such comments to the implementation to verify if the implementation is correct
Example: This method is possibly buggy because the implementation does not seem to match the comment. In this case the comment could help the reader to detect the bug.
/** Removes all spaces from the {@code input} */
void compact(String input){
input.trim();
}
👍 Why : The rationale for the current implementation.
Example: Without this comment, the reader will not know the reason for calling this method.
// Remove spaces to comply with IE23.5 formatting rules
compact(input);
👎 How : The explanation for how the code works. This should already be apparent from the code, if the code is self-explanatory. Adding comments to explain the same thing is redundant.
Example:
Bad Reason: Comment explains how the code works.
// return true if both left end and right end are correct or the size has not incremented
return (left && right) || (input.size() == size);
Good Reason: Code refactored to be self-explanatory. Comment no longer needed.
boolean isSameSize = (input.size() == size) ;
return (isLeftEndCorrect && isRightEndCorrect) || isSameSize;
null
B. Depth and completeness of the major feature
Evaluates: How good is your Quality Assurance?
Based on: 1. your test code 2. our own manual testing 3. your performance in the two Practical Exams (PE), 4. bugs found during PE.
Relevant: [
What: The v1.3 is subjected to a round of peer acceptance/system testing, also called the Practical Exam Round 1 (PE-1). This round of testing will be graded similar to the
When, where: 45 minute slot at the end of week 11 lecture, in the Lecture venue
Objectives:
- Evaluate your,
- manual testing skills
- product evaluation skills
- effort estimation skills
- Peer-evaluate your
- product design
- implementation effort
- documentation quality
When, where: Week 13 lecture
Grading:
- Your performance in the practical exams will be considered for your final grade (under the QA category and under Implementation category, about 10 marks in total).
- You will be graded based on your effectiveness as a tester (e.g., the percentage of the bugs you found, the nature of the bugs you found) and how far off your evaluation/estimates are from the evaluator consensus. Explanation: we understand that you have limited expertise in this area; hence, we penalize only if your inputs don't seem to be based on a sincere effort to test/evaluate.
- The bugs found in your product by others will affect your v1.4 marks. You will be given a chance to reject false-positive bug reports.
Preparation:
-
Ensure that you can access the relevant issue tracker given below:
-- for PE-1: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1
-- for PE-2: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2- These are private repos!. If you cannot access the relevant repo, you may not have accepted the invitation to join the GitHub org used by the module. Go to https://github.com/orgs/nusCS2113-AY1819S1/invitation to accept the invitation.
- If you cannot find the invitation, post in our forum.
-
Ensure you have access to a computer that is able to run module projects e.g. has the right Java version.
-
Have a good screen grab tool with annotation features so that you can quickly take a screenshot of a bug, annotate it, and post in the issue tracker.
- 💡 You can use Ctrl+V to paste a picture from the clipboard into a text box in GitHub issue tracker.
-
Charge your computer before coming to the PE session. The testing venue may not have enough charging points.
During:
- Take note of your team to test. It will be given to you by the teaching team (distributed via IVLE gradebook).
- Download from IVLE all files submitted by the team (i.e. jar file, User Guide, Developer Guide, and Project Portfolio Pages) into an empty folder.
- [~45 minutes] Test the product and report bugs as described below:
Testing instructions for PE-1 and PE-2
-
What to test:
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
helpcommand). - Do system testing first i.e., does the product work as specified by the documentation?. If there is time left, you can do acceptance testing as well i.e., does the product solve the problem it claims to solve?.
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
- PE-2 (at v1.4):
- Test the product based on the Developer Guide (Appendix named Instructions for Manual Testing) and the User Guide. The testing instructions in the Developer Guide can provide you some guidance but if you follow those instructions strictly, you are unlikely to find many bugs. You can deviate from the instructions to probe areas that are more likely to have bugs.
- Do system testing only i.e., verify actual behavior against documented behavior. Do not do acceptance testing.
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
-
What not to test:
- Omit features that are driven by GUI inputs (e.g. buttons, menus, etc.) Reason: Only CLI-driven features can earn credit, as per given project constraints. Some features might have both a GUI-driven and CLI-driven ways to invoke them, in which case test only the CLI-driven way of invoking it.
- Omit feature that existed in AB-4.
-
These are considered bugs:
- Behavior differs from the User Guide
- A legitimate user behavior is not handled e.g. incorrect commands, extra parameters
- Behavior is not specified and differs from normal expectations e.g. error message does not match the error
- Problems in the User Guide e.g., missing/incorrect info
-
Where to report bugs: Post bug in the following issue trackers (not in the team's repo):
- PE-1 (at v1.3): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2.
-
Bug report format:
- Post bugs as you find them (i.e., do not wait to post all bugs at the end) because the issue tracker will close exactly at the end of the allocated time.
- Do not use team ID in bug reports. Reason: to prevent others copying your bug reports
- Each bug should be a separate issue.
- Write good quality bug reports; poor quality or incorrect bug reports will not earn credit.
- Use a descriptive title.
- Give a good description of the bug with steps to reproduce and screenshots.
- Use the template(s) in the issue tracker as much as possible.
- Assign a severity to the bug report. Bug report without a priority label are considered
severity.Low(lower severity bugs earn lower credit):
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
About posting suggestions:
- PE-1 (at v1.3): You can also post suggestions on how to improve the product. 💡 Be diplomatic when reporting bugs or suggesting improvements. For example, instead of criticising the current behavior, simply suggest alternatives to consider.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): Do not post suggestions.
-
If the product doesn't work at all: If the product fails catastrophically e.g., cannot even launch, contact the lecturer immediately to obtain a new product to test.
-
[~45 minutes] Evaluate the following aspects. Note down your evaluation in a hard copy (as a backup). Submit via TEAMMATES.
-
A. Cohesiveness of product features []: Do the features fit together and match the stated target user and the value proposition?
unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: One of these- target user is too general i.e. wider than AB4
- target user and/or value proposition is not clear from the user guide
- features don't seem to fit together for the most part
medium: Some features fit together but some don't.high: All features fit together but the features are not very high value to the target user.excellent: The target user is clearly defined (not too general) and almost all new features are of high-value to the target user. i.e. the product is very attractive to the target user.
-
B. Quality of user docs []: Evaluate based on the parts of the user guide written by the person, as reproduced in the project portfolio. Evaluate from an end-user perspective.
unable to judge: Less than 1 page worth of UG content written by the student.low: Hard to understand, often inaccurate or missing important information.medium: Needs some effort to understand; some information is missing.high: Mostly easy to follow. Only a few areas need improvements.excellent: Easy to follow and accurate. Just enough information, visuals, examples etc. (not too much either).
-
C. Quality of developer docs []: Evaluate based on the developer docs cited/reproduced in the respective project portfolio page. Evaluate from the perspective of a new developer trying to understand how the features are implemented.
unable to judge: One of these- no content at all.
- less than 0.5 pages worth of content.
- other problems in the document e.g. looks like included wrong content.
low: One of these- Very small amount of content (i.e., 0.5 - 1 page).
- Hardly any use to the reader (i.e., content doesn't make much sense or redundant).
- Uses ad-hoc diagrams where UML diagrams could have been used instead.
- Multiple notation errors in UML diagrams.
medium: Some diagrams, some descriptions, but does not help the reader that much e.g. overly complicated diagrams.high: Enough diagrams (at lest two kinds of UML diagrams used) and enough descriptions (about 2 pages worth) but explanations are not always easy to follow.excellent: Easy to follow. Just enough information (not too much). Minimum repetition of content/diagrams. Good use of diagrams to complement text descriptions. Easy to understand diagrams with just enough details rather than very complicated diagrams that are hard to understand.
-
D. Depth of feature []: Evaluate the feature done by the student for difficulty, depth, and completeness. Note: examples given below assumes AB4 did not have the commands
edit,undo, andredo.unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: An easy feature e.g. make the existing find command case insensitive.medium: Moderately difficult feature, barely acceptable implementation e.g. an edit command that requires the user to type all fields, even the ones that are not being edited.high: One of the below- A moderately difficult feature but fully implemented e.g. an edit command that allows editing any field.
- A difficult feature with a reasonable implementation but some aspects are not covered undo/redo command that only allows a single undo/redo.
excellent: A difficult feature, all reasonable aspects are fully implemented undo/redo command that allows multiple undo/redo.
-
E. Amount of work []: Evaluate the amount of work, on a scale of 0 to 30.
- Consider this PR (
historycommand) as 5 units of effort which means this PR (undo/redocommand) is about 15 points of effort. Given that 30 points matches an effort twice as that needed for theundo/redofeature (which was given as an example of anAgrade project), we expect most students to be have efforts lower than 20. - Consider the main feature only. Exclude GUI inputs, but consider GUI outputs of the feature. Count all implementation/testing/documentation work as mentioned in that person's portfolio page. Also look at the actual code written by the person. We understand that it is not possible to know exactly which part of the code is for the main feature; make a best guess judgement call based on the available info.
- Do not give a high value just to be nice. If your estimate is wildly inaccurate, it means you are unable to estimate the effort required to implement a feature in a project that you are supposed to know well at this point. You will lose marks if that is the case.
- Consider this PR (
-
Bug Review Period:
There will be a review period for you to respond to the bug reports you received.
Duration: The review period will start around 1 day after the PE (exact time to be announced) and will last until the following Tuesday midnight.
Bug reviewing is recommended to be done as a team as some of the decisions need team consensus.
Instructions for Reviewing Bug Reports
-
First, don't freak out if there are lot of bug reports. Many can be duplicates and some can be false positives. In any case, we anticipate that all of these products will have some bugs and our penalty for bugs is not harsh. Furthermore, it depends on the severity of the bug. Some bug may not even be penalized.
-
Do not edit the subject or the description. Do not close bug reports. Your response (if any) should be added as a comment.
-
If the bug is reported multiple times, mark all copies EXCEPT one as duplicates using the
duplicatetag (if the duplicates have different severity levels, you should keep the one with the highest severity). In addition, use this technique to indicate which issue they are duplicates of. Duplicates can be omitted from processing steps given below. -
If a bug seems to be for a different product (i.e. wrongly assigned to your team), let us know (email prof).
-
Decide if it is a real bug and apply ONLY one of these labels.
Response Labels:
response.Accepted: You accept it as a bug.response.Rejected: What tester thought as a bug is in fact expected behavior. ❗️ The penalty for rejecting a bug using an unjustifiable explanation is higher than the penalty if the same bug was accepted. You can also reject bugs that you inherited from AB4.response.CannotReproduce: You are unable to reproduce the behavior reported in the bug after multiple tries.response.IssueUnclear: The issue description is not clear.
- If applicable, decide the type of bug. Bugs without
type-are consideredtype-FunctionalityBugby default (which are liable to a heavier penalty):
Bug Type Labels:
type-FunctionalityBug: the bug is a flaw in how the product works.type-DocumentationBug: the bug is in the documentation.
- If you disagree with the original severity assigned to the bug, you may change it to the correct level, in which case add a comment justifying the change. All such changes will be double-checked by the teaching team and unreasonable lowering of severity will be penalized extra.:
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
Decide who should fix the bug. Use the
Assigneesfield to assign the issue to that person(s). There is no need to actually fix the bug though. It's simply an indication/acceptance of responsibility. If there is no assignee, we will distribute the penalty for that bug (if any) among all team members. -
Add an explanatory comment explaining your choice of labels and assignees.
Grading: Taking part in the PE-1 is strongly encouraged as it can affect your grade in the following ways.
- We will consider your performance in both PE-1 as well as PE-2 when grading.
- You will be graded based on your effectiveness as a tester (e.g., the percentage of the bugs you found, the nature of the bugs you found) and how far off your evaluation/estimates are from the evaluator consensus. Explanation: we understand that you have limited expertise in this area; hence, we penalize only if your inputs don't seem to be based on a sincere effort to test/evaluate.
- There is no penalty for bugs reported in your product. Every bug you find is a win-win for you and the team whose product you are testing.
Objectives:
- To train you to do manual testing, bug reporting, bug
triaging, bug fixing, communicating with users/testers/developers, evaluating products etc. - To help you improve your product before the final submission.
Preparation:
-
Ensure that you can access the relevant issue tracker given below:
-- for PE-1: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1
-- for PE-2: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2- These are private repos!. If you cannot access the relevant repo, you may not have accepted the invitation to join the GitHub org used by the module. Go to https://github.com/orgs/nusCS2113-AY1819S1/invitation to accept the invitation.
- If you cannot find the invitation, post in our forum.
-
Ensure you have access to a computer that is able to run module projects e.g. has the right Java version.
-
Have a good screen grab tool with annotation features so that you can quickly take a screenshot of a bug, annotate it, and post in the issue tracker.
- 💡 You can use Ctrl+V to paste a picture from the clipboard into a text box in GitHub issue tracker.
-
Charge your computer before coming to the PE session. The testing venue may not have enough charging points.
During the session:
- Take note of your team to test. Distributed via IVLE gradebook.
- Download the latest jar file from the team's GitHub page. Copy it to an empty folder.
Testing instructions for PE-1 and PE-2
-
What to test:
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
helpcommand). - Do system testing first i.e., does the product work as specified by the documentation?. If there is time left, you can do acceptance testing as well i.e., does the product solve the problem it claims to solve?.
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
- PE-2 (at v1.4):
- Test the product based on the Developer Guide (Appendix named Instructions for Manual Testing) and the User Guide. The testing instructions in the Developer Guide can provide you some guidance but if you follow those instructions strictly, you are unlikely to find many bugs. You can deviate from the instructions to probe areas that are more likely to have bugs.
- Do system testing only i.e., verify actual behavior against documented behavior. Do not do acceptance testing.
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
-
What not to test:
- Omit features that are driven by GUI inputs (e.g. buttons, menus, etc.) Reason: Only CLI-driven features can earn credit, as per given project constraints. Some features might have both a GUI-driven and CLI-driven ways to invoke them, in which case test only the CLI-driven way of invoking it.
- Omit feature that existed in AB-4.
-
These are considered bugs:
- Behavior differs from the User Guide
- A legitimate user behavior is not handled e.g. incorrect commands, extra parameters
- Behavior is not specified and differs from normal expectations e.g. error message does not match the error
- Problems in the User Guide e.g., missing/incorrect info
-
Where to report bugs: Post bug in the following issue trackers (not in the team's repo):
- PE-1 (at v1.3): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2.
-
Bug report format:
- Post bugs as you find them (i.e., do not wait to post all bugs at the end) because the issue tracker will close exactly at the end of the allocated time.
- Do not use team ID in bug reports. Reason: to prevent others copying your bug reports
- Each bug should be a separate issue.
- Write good quality bug reports; poor quality or incorrect bug reports will not earn credit.
- Use a descriptive title.
- Give a good description of the bug with steps to reproduce and screenshots.
- Use the template(s) in the issue tracker as much as possible.
- Assign a severity to the bug report. Bug report without a priority label are considered
severity.Low(lower severity bugs earn lower credit):
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
About posting suggestions:
- PE-1 (at v1.3): You can also post suggestions on how to improve the product. 💡 Be diplomatic when reporting bugs or suggesting improvements. For example, instead of criticising the current behavior, simply suggest alternatives to consider.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): Do not post suggestions.
-
If the product doesn't work at all: If the product fails catastrophically e.g., cannot even launch, contact the lecturer immediately to obtain a new product to test.
At the end of the project each student is required to submit a Project Portfolio Page.
-
Objective:
- For you to use (e.g. in your resume) as a well-documented data point of your SE experience
- For us to use as a data point to evaluate your,
- contributions to the project
- your documentation skills
-
Sections to include:
-
Overview: A short overview of your product to provide some context to the reader.
-
Summary of Contributions:
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
https://nuscs2113-ay1819s1.github.io/dashboard/#=undefined&search=githbub_username_in_lower_case(replacegithbub_username_in_lower_casewith your actual username in lower case e.g.,johndoe). This link is also available in the Project List Page -- linked to the icon under your photo. - Main feature implemented: A summary of the main feature you implemented
- Other contributions:
- Contributions to project management e.g., setting up project tools, managing releases, managing issue tracker etc.
- Evidence of helping others e.g. responses you posted in our forum, bugs you reported in other team's products,
- Evidence of technical leadership e.g. sharing useful information in the forum
- [Optional] Other minor enhancements: If you have other enhancements that you implemented, which are not related to your main feature, you can include it here. If you have written a significant amount of code that can be advertised as a feature by itself, but does not belong to your main feature, you can choose to include it as a part of the optional enhancements.
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
-
Contributions to the User Guide: Reproduce the parts in the User Guide that you wrote. This can include features you implemented as well as features you propose to implement.
The purpose of allowing you to include proposed features is to provide you more flexibility to show your documentation skills. e.g. you can bring in a proposed feature just to give you an opportunity to use a UML diagram type not used by the actual features. -
Contributions to the Developer Guide: Reproduce the parts in the Developer Guide that you wrote. Ensure there is enough content to evaluate your technical documentation skills and UML modelling skills. You can include descriptions of your design/implementations, possible alternatives, pros and cons of alternatives, etc.
-
If you plan to use the PPP in your Resume, you can also include your SE work outside of the module (will not be graded)
-
-
Format:
-
File name:
docs/team/githbub_username_in_lower_case.adoce.g.,docs/team/johndoe.adoc -
Follow the example in the AddressBook-Level4, but ignore the following two lines in it.
- Minor enhancement: added a history command that allows the user to navigate to previous commands using up/down keys.
- Code contributed: [Functional code] [Test code] {give links to collated code files}
-
💡 You can use the Asciidoc's
includefeature to include sections from the developer guide or the user guide in your PPP. Follow the example in the sample. -
It is assumed that all contents in the PPP were written primarily by you. If any section is written by someone else e.g. someone else wrote described the feature in the User Guide but you implemented the feature, clearly state that the section was written by someone else (e.g.
Start of Extract [from: User Guide] written by Jane Doe). Reason: Your writing skills will be evaluated based on the PPP -
Page limit: If you have more content than the limit given below, shorten (or omit some content) so that you do not exceed the page limit. Having too much content in the PPP will be viewed unfavorably during grading. Note: the page limits given below are after converting to PDF format. The actual amount of content you require is actually less than what these numbers suggest because the HTML → PDF conversion adds a lot of spacing around content.
Content Limit Overview + Summary of contributions 0.5-1 Contributions to the User Guide 1-3 Contributions to the Developer Guide 3-6 Total 5-10
-
After the session:
- We'll transfer the relevant bug reports to your repo over the weekend. Once you have received the bug reports for your product, it is up to you to decide whether you will act on reported issues before the final submission v1.4. For some issues, the correct decision could be to reject or postpone to a version beyond v1.4.
- You can post in the issue thread to communicate with the tester e.g. to ask for more info, etc. However, the tester is not obliged to respond.
- 💡 Do not argue with the issue reporter to try to convince that person that your way is correct/better. If at all, you can gently explain the rationale for the current behavior but do not waste time getting involved in long arguments. If you think the suggestion/bug is unreasonable, just thank the reporter for their view and close the issue.
Relevant: [
Objectives:
- Evaluate your,
- manual testing skills
- product evaluation skills
- effort estimation skills
- Peer-evaluate your
- product design
- implementation effort
- documentation quality
When, where: Week 13 lecture
Grading:
- Your performance in the practical exams will be considered for your final grade (under the QA category and under Implementation category, about 10 marks in total).
- You will be graded based on your effectiveness as a tester (e.g., the percentage of the bugs you found, the nature of the bugs you found) and how far off your evaluation/estimates are from the evaluator consensus. Explanation: we understand that you have limited expertise in this area; hence, we penalize only if your inputs don't seem to be based on a sincere effort to test/evaluate.
- The bugs found in your product by others will affect your v1.4 marks. You will be given a chance to reject false-positive bug reports.
Preparation:
-
Ensure that you can access the relevant issue tracker given below:
-- for PE-1: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1
-- for PE-2: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2- These are private repos!. If you cannot access the relevant repo, you may not have accepted the invitation to join the GitHub org used by the module. Go to https://github.com/orgs/nusCS2113-AY1819S1/invitation to accept the invitation.
- If you cannot find the invitation, post in our forum.
-
Ensure you have access to a computer that is able to run module projects e.g. has the right Java version.
-
Have a good screen grab tool with annotation features so that you can quickly take a screenshot of a bug, annotate it, and post in the issue tracker.
- 💡 You can use Ctrl+V to paste a picture from the clipboard into a text box in GitHub issue tracker.
-
Charge your computer before coming to the PE session. The testing venue may not have enough charging points.
During:
- Take note of your team to test. It will be given to you by the teaching team (distributed via IVLE gradebook).
- Download from IVLE all files submitted by the team (i.e. jar file, User Guide, Developer Guide, and Project Portfolio Pages) into an empty folder.
- [~45 minutes] Test the product and report bugs as described below:
Testing instructions for PE-1 and PE-2
-
What to test:
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
helpcommand). - Do system testing first i.e., does the product work as specified by the documentation?. If there is time left, you can do acceptance testing as well i.e., does the product solve the problem it claims to solve?.
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
- PE-2 (at v1.4):
- Test the product based on the Developer Guide (Appendix named Instructions for Manual Testing) and the User Guide. The testing instructions in the Developer Guide can provide you some guidance but if you follow those instructions strictly, you are unlikely to find many bugs. You can deviate from the instructions to probe areas that are more likely to have bugs.
- Do system testing only i.e., verify actual behavior against documented behavior. Do not do acceptance testing.
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
-
What not to test:
- Omit features that are driven by GUI inputs (e.g. buttons, menus, etc.) Reason: Only CLI-driven features can earn credit, as per given project constraints. Some features might have both a GUI-driven and CLI-driven ways to invoke them, in which case test only the CLI-driven way of invoking it.
- Omit feature that existed in AB-4.
-
These are considered bugs:
- Behavior differs from the User Guide
- A legitimate user behavior is not handled e.g. incorrect commands, extra parameters
- Behavior is not specified and differs from normal expectations e.g. error message does not match the error
- Problems in the User Guide e.g., missing/incorrect info
-
Where to report bugs: Post bug in the following issue trackers (not in the team's repo):
- PE-1 (at v1.3): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2.
-
Bug report format:
- Post bugs as you find them (i.e., do not wait to post all bugs at the end) because the issue tracker will close exactly at the end of the allocated time.
- Do not use team ID in bug reports. Reason: to prevent others copying your bug reports
- Each bug should be a separate issue.
- Write good quality bug reports; poor quality or incorrect bug reports will not earn credit.
- Use a descriptive title.
- Give a good description of the bug with steps to reproduce and screenshots.
- Use the template(s) in the issue tracker as much as possible.
- Assign a severity to the bug report. Bug report without a priority label are considered
severity.Low(lower severity bugs earn lower credit):
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
About posting suggestions:
- PE-1 (at v1.3): You can also post suggestions on how to improve the product. 💡 Be diplomatic when reporting bugs or suggesting improvements. For example, instead of criticising the current behavior, simply suggest alternatives to consider.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): Do not post suggestions.
-
If the product doesn't work at all: If the product fails catastrophically e.g., cannot even launch, contact the lecturer immediately to obtain a new product to test.
-
[~45 minutes] Evaluate the following aspects. Note down your evaluation in a hard copy (as a backup). Submit via TEAMMATES.
-
A. Cohesiveness of product features []: Do the features fit together and match the stated target user and the value proposition?
unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: One of these- target user is too general i.e. wider than AB4
- target user and/or value proposition is not clear from the user guide
- features don't seem to fit together for the most part
medium: Some features fit together but some don't.high: All features fit together but the features are not very high value to the target user.excellent: The target user is clearly defined (not too general) and almost all new features are of high-value to the target user. i.e. the product is very attractive to the target user.
-
B. Quality of user docs []: Evaluate based on the parts of the user guide written by the person, as reproduced in the project portfolio. Evaluate from an end-user perspective.
unable to judge: Less than 1 page worth of UG content written by the student.low: Hard to understand, often inaccurate or missing important information.medium: Needs some effort to understand; some information is missing.high: Mostly easy to follow. Only a few areas need improvements.excellent: Easy to follow and accurate. Just enough information, visuals, examples etc. (not too much either).
-
C. Quality of developer docs []: Evaluate based on the developer docs cited/reproduced in the respective project portfolio page. Evaluate from the perspective of a new developer trying to understand how the features are implemented.
unable to judge: One of these- no content at all.
- less than 0.5 pages worth of content.
- other problems in the document e.g. looks like included wrong content.
low: One of these- Very small amount of content (i.e., 0.5 - 1 page).
- Hardly any use to the reader (i.e., content doesn't make much sense or redundant).
- Uses ad-hoc diagrams where UML diagrams could have been used instead.
- Multiple notation errors in UML diagrams.
medium: Some diagrams, some descriptions, but does not help the reader that much e.g. overly complicated diagrams.high: Enough diagrams (at lest two kinds of UML diagrams used) and enough descriptions (about 2 pages worth) but explanations are not always easy to follow.excellent: Easy to follow. Just enough information (not too much). Minimum repetition of content/diagrams. Good use of diagrams to complement text descriptions. Easy to understand diagrams with just enough details rather than very complicated diagrams that are hard to understand.
-
D. Depth of feature []: Evaluate the feature done by the student for difficulty, depth, and completeness. Note: examples given below assumes AB4 did not have the commands
edit,undo, andredo.unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: An easy feature e.g. make the existing find command case insensitive.medium: Moderately difficult feature, barely acceptable implementation e.g. an edit command that requires the user to type all fields, even the ones that are not being edited.high: One of the below- A moderately difficult feature but fully implemented e.g. an edit command that allows editing any field.
- A difficult feature with a reasonable implementation but some aspects are not covered undo/redo command that only allows a single undo/redo.
excellent: A difficult feature, all reasonable aspects are fully implemented undo/redo command that allows multiple undo/redo.
-
E. Amount of work []: Evaluate the amount of work, on a scale of 0 to 30.
- Consider this PR (
historycommand) as 5 units of effort which means this PR (undo/redocommand) is about 15 points of effort. Given that 30 points matches an effort twice as that needed for theundo/redofeature (which was given as an example of anAgrade project), we expect most students to be have efforts lower than 20. - Consider the main feature only. Exclude GUI inputs, but consider GUI outputs of the feature. Count all implementation/testing/documentation work as mentioned in that person's portfolio page. Also look at the actual code written by the person. We understand that it is not possible to know exactly which part of the code is for the main feature; make a best guess judgement call based on the available info.
- Do not give a high value just to be nice. If your estimate is wildly inaccurate, it means you are unable to estimate the effort required to implement a feature in a project that you are supposed to know well at this point. You will lose marks if that is the case.
- Consider this PR (
-
Bug Review Period:
There will be a review period for you to respond to the bug reports you received.
Duration: The review period will start around 1 day after the PE (exact time to be announced) and will last until the following Tuesday midnight.
Bug reviewing is recommended to be done as a team as some of the decisions need team consensus.
Instructions for Reviewing Bug Reports
-
First, don't freak out if there are lot of bug reports. Many can be duplicates and some can be false positives. In any case, we anticipate that all of these products will have some bugs and our penalty for bugs is not harsh. Furthermore, it depends on the severity of the bug. Some bug may not even be penalized.
-
Do not edit the subject or the description. Do not close bug reports. Your response (if any) should be added as a comment.
-
If the bug is reported multiple times, mark all copies EXCEPT one as duplicates using the
duplicatetag (if the duplicates have different severity levels, you should keep the one with the highest severity). In addition, use this technique to indicate which issue they are duplicates of. Duplicates can be omitted from processing steps given below. -
If a bug seems to be for a different product (i.e. wrongly assigned to your team), let us know (email prof).
-
Decide if it is a real bug and apply ONLY one of these labels.
Response Labels:
response.Accepted: You accept it as a bug.response.Rejected: What tester thought as a bug is in fact expected behavior. ❗️ The penalty for rejecting a bug using an unjustifiable explanation is higher than the penalty if the same bug was accepted. You can also reject bugs that you inherited from AB4.response.CannotReproduce: You are unable to reproduce the behavior reported in the bug after multiple tries.response.IssueUnclear: The issue description is not clear.
- If applicable, decide the type of bug. Bugs without
type-are consideredtype-FunctionalityBugby default (which are liable to a heavier penalty):
Bug Type Labels:
type-FunctionalityBug: the bug is a flaw in how the product works.type-DocumentationBug: the bug is in the documentation.
- If you disagree with the original severity assigned to the bug, you may change it to the correct level, in which case add a comment justifying the change. All such changes will be double-checked by the teaching team and unreasonable lowering of severity will be penalized extra.:
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
Decide who should fix the bug. Use the
Assigneesfield to assign the issue to that person(s). There is no need to actually fix the bug though. It's simply an indication/acceptance of responsibility. If there is no assignee, we will distribute the penalty for that bug (if any) among all team members. -
Add an explanatory comment explaining your choice of labels and assignees.
- There is no requirement for a minimum coverage level. Note that in a production environment you are often required to have at least 90% of the code covered by tests. In this project, it can be less. The less coverage you have, the higher the risk of regression bugs, which will cost marks if not fixed before the final submission.
- You must write some tests so that we can evaluate your ability to write tests.
- How much of each type of testing should you do? We expect you to decide. You learned different types of testing and what they try to achieve. Based on that, you should decide how much of each type is required. Similarly, you can decide to what extent you want to automate tests, depending on the benefits and the effort required.
- Applying TDD is optional. If you plan to test something, it is better to apply TDD because TDD ensures that you write functional code in a testable way. If you do it the normal way, you often find that it is hard to test the functional code because the code has low testability.
Evaluates: How well does your user guide achieves its objectives?
Based on: the relevant sections of your project portfolio. Criteria considered:
- Explanation should be clear and written to match the audience.
- Good use of visuals to complement text.
A. Process:
Evaluates: How well you did in project management related aspects of the project, as an individual and as a team
Based on: Supervisor observations of project milestones and GitHub data.
Milestones need to be reached the midnight before of the tutorial for it to be counted as achieved. To get a good grade this aspect, achieve recommended weekly progress in at least 6/10 weeks.
Other criteria:
- Good use of GitHub milestones
- Good use of GitHub release mechanism
- Good version control, based on the repo
- Reasonable attempt to use the forking workflow
- Good task definition, assignment and tracking, based on the issue tracker
- Good use of buffers (opposite: everything at the last minute)
- Project done iteratively and incrementally (opposite: doing most of the work in one big burst)
B. Team-based tasks:
Evaluates: How much you contributed to common team-based tasks
Based on: peer evaluations and tutor observations
Relevant: [
Here is a non-exhaustive list of team-tasks:
- Necessary general code enhancements e.g.,
- Work related to renaming the product
- Work related to changing the product icon
- Morphing the product into a different product
- Setting up the GitHub, Travis, AppVeyor, etc.,
- Maintaining the issue tracker
- Release management
- Updating user/developer docs that are not specific to a feature e.g. documenting the target user profile
- Incorporating more useful tools/libraries/frameworks into the product or the project workflow (e.g. automate more aspects of the project workflow using a GitHub plugin)
Policy on following instructions
When working with others, especially in a large class such as CS2113/T, it is very important that you adhere to standards, policies, and instructions imposed on everyone. Not doing so creates unnecessary headaches for everyone and puts your work attitude in a negative light. That is why we penalize repeated violations of instructions. On the other hand we do understand that humans are liable to make mistakes. That is why we only penalize repeated or frequent mistakes.
We use the TEAMMATES online peer evaluation system to conduct several rounds of peer-evaluations. All peer evaluations will be taken into account when determining your participation marks. The system also allows you to give anonymous feedback to your teammates.
Extra Requirements: [considered for participation marks]
- ❗️ Submitting peer evaluations is compulsory.
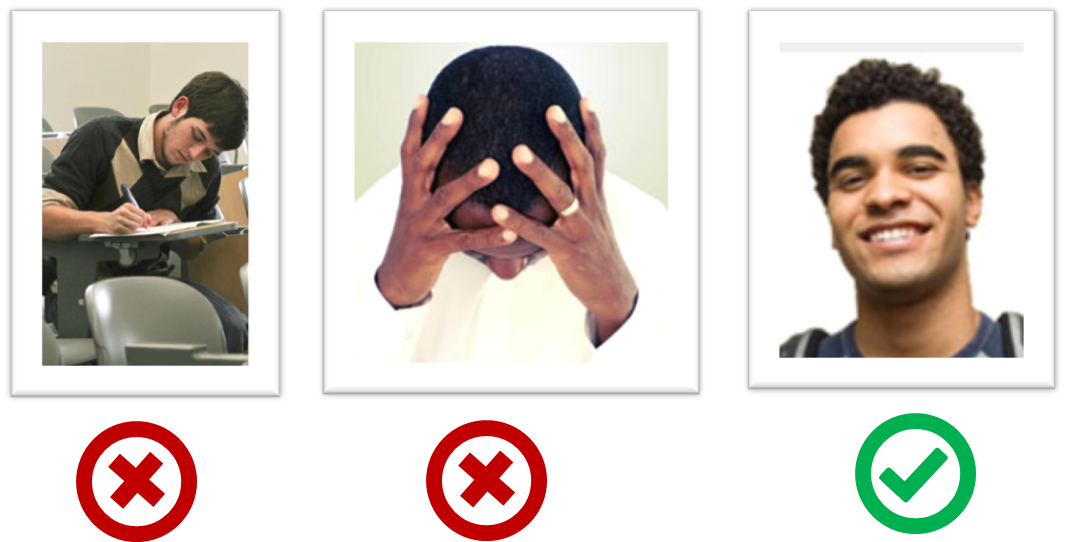
- 💡 TEAMMATES normally allows students to access it without using Google login. In this module, we encourage (but not require) you to login to TEAMMATES using your Google account and complete your profile with a
suitable profile photo . Reason: CS2113/T is a big class. This profile helps us to remember you better, even after the module is over.
-
The purpose of the profile photo is for the teaching team to identify you. Therefore, you should choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Some examples can be seen in the 'Teaching team' page. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.

-
If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you can request permission to omit your photo from the page by writing to prof.
Peer evaluation criteria: professional conduct
- Professional Communication :
- Communicates sufficiently and professionally. e.g. Does not use offensive language or excessive slang in project communications.
- Responds to communication from team members in a timely manner (e.g. within 24 hours).
- Punctuality: Does not cause others to waste time or slow down project progress by frequent tardiness.
- Dependability: Promises what can be done, and delivers what was promised.
- Effort: Puts in sufficient effort to, and tries their best to keep up with the module/project pace. Seeks help from others when necessary.
- Quality: Does not deliver work products that seem to be below the student's competence level i.e. tries their best to make the work product as high quality as possible within her competency level.
- Meticulousness:
- Rarely overlooks submission requirements.
- Rarely misses compulsory module activities such as completing the TEAMMATES profile or peer review.
- Teamwork: How willing are you to act as part of a team, contribute to team-level tasks, adhere to team decisions, etc.
Peer evaluation criteria: competency
- Technical Competency: Able to gain competency in all the required tools and techniques.
- Mentoring skills: Helps others when possible. Able to mentor others well.
- Communication skills: Able to communicate (written and spoken) well. Takes initiative in discussions.
Giving constructive feedback to others is a valuable skill for software engineers. It is also an intended learning outcome of this module. Half-hearted/trivial feedback will not earn participation marks.
Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Assume you are giving feedback to a colleague, not a friend. Keep the tone of your feedback reasonably professional. Do not use offensive language or slang.
- The feedback should be honest and consistent. Giving positive qualitative feedback (e.g.
Thanks for all the hard work!and negative ratings (e.g.Equal share - 40%) to the same team member is not being honest. - State your expectations early. All too often students give positive/neutral feedback early (hoping that the team member will improve later) and trash the team member in the final evaluation (because the he/she did not improve as expected). However, this could be confusing to the recipient. It is better to give negative feedback early so that the team member gets a clear signal that he/she needs to improve.
The final peer evaluation (in week 13) is graded. In that peer-evaluation you will be asked to evaluate the work of your team members and another team. The quality and accuracy of your evaluation will affect your grade and your evaluations will be considered as a data point in determining the grade of the team members.
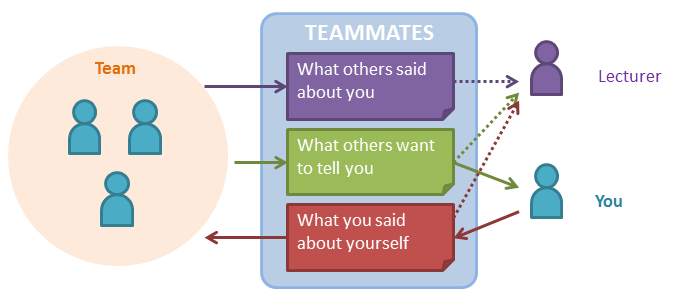
Relevant: [
10 marks allocated for participation can be earned in the following ways (there are ~28 available marks to choose from):
-
Good peer ratings - Criteria for professional conduct (1 mark for each criterion, max 7)
- Competency criteria (2 marks for each, max 6)
- In-lecture quizzes
- In-lecture quizzes, roughly two questions each week (0.5 each, max 10 marks)
- Module admin tasks done on time and as instructed
- Peer evaluations (1 mark each)
- Pre-module survey (1 mark)
- Enhanced AB1-AB3: 2 mark each
Relevant: [
Peer evaluation criteria: professional conduct
- Professional Communication :
- Communicates sufficiently and professionally. e.g. Does not use offensive language or excessive slang in project communications.
- Responds to communication from team members in a timely manner (e.g. within 24 hours).
- Punctuality: Does not cause others to waste time or slow down project progress by frequent tardiness.
- Dependability: Promises what can be done, and delivers what was promised.
- Effort: Puts in sufficient effort to, and tries their best to keep up with the module/project pace. Seeks help from others when necessary.
- Quality: Does not deliver work products that seem to be below the student's competence level i.e. tries their best to make the work product as high quality as possible within her competency level.
- Meticulousness:
- Rarely overlooks submission requirements.
- Rarely misses compulsory module activities such as completing the TEAMMATES profile or peer review.
- Teamwork: How willing are you to act as part of a team, contribute to team-level tasks, adhere to team decisions, etc.
Peer evaluation criteria: competency
- Technical Competency: Able to gain competency in all the required tools and techniques.
- Mentoring skills: Helps others when possible. Able to mentor others well.
- Communication skills: Able to communicate (written and spoken) well. Takes initiative in discussions.
Relevant: [
There is no midterm.
The final exam has two parts:
- Part 1: MCQ questions (30 minutes, 25 marks)
- Part 2: Essay questions (1 hour 30 min, 30 marks)
Both papers will be given to you at the start but you need to answer Part 1 first (i.e. MCQ paper). It will be collected 30 min after the exam start time (even if arrived late for the exam). You are free to start part 2 early if you finish Part 1 early.
Final Exam: Part 1 (MCQ)
Each MCQ question gives you a statement to evaluate.
An example statement
Testing is a Q&A activity
Unless stated otherwise, the meaning of answer options are
A. True
B. False
The exam paper has 50 questions. All questions carry equal marks.
The weightage of the Part 1 of the final exam is 25 marks out of the total score of 100.
Note that you have slightly more than ½ minute for each question, which means you need to go through the questions fairly quickly.
Given the fast pace required by the paper, to be fair to all students, you will not be allowed to clarify doubts about questions (in Part 1) by talking to invigilators.
Questions in Part 1 are confidential. You are not allowed to reveal Part 1 content to anyone after the exam. All pages of the assessment paper are to be returned at the end of the exam.
You will be given OCR forms to indicate your answers for Part 1.
The paper is open-book: you may bring any printed or written materials to the exam in hard copy format. However, given the fast pace required by Part 1, you will not have time left to refer notes during that part of the exam.
💡 Mark the OCR form as you go, rather than planning to transfer your answers to the OCR form near the end. Reason: Given there are 50 questions and only 30 mins, it will be hard to estimate how much time you need to mass-transfer all answers to OCR forms.
💡 Write the answer in the exam paper as well as marking it in the OCR form. Reason: It will reduce the chance of missing a question. Furthermore, in case you missed a question, it will help you correct the OCR form quickly.
💡 We have tried to avoid deliberately misleading/tricky questions. If a question seems to take a very long time to figure out, you are probably over-thinking it.
Final Exam: Part 2 (Essay)
Unlike in part 1, you can ask invigilators for clarifications if you found a question to be unclear in part 2.
Yes, you may use pencils when answering part 2.
The weightage of the Part 2 of the final exam is 15 marks out of the total score of 100.
Resources
Past exam papers uploaded on IVLE
Relevant: [
Note that project grading is not competitive (not bell curved). CS2113T projects will be assessed separately from CS2113 projects. This is to account for the perceived difference in workload. Given below is the marking scheme.
Total: 50 marks ( 40 individual marks + 10 team marks)
Evaluates: How well do your features fit together to form a cohesive product (not how many features or how big the features are)?
Based on: user guide and the product demo. The quality of the demo will be factored in as well.
❗️ Feature that fits well with the other features will earn more marks.
Evaluates:
A. Code quality/quantity:
How good your implementation is, in terms of the quality and the quantity of the code you have written yourself.
Based on: an inspection of the collated code (obtained from Reposense).
-
Ensure your code has at least some evidence of these (see here for more info)
- logging
- exceptions
- assertions
- defensive coding
-
Ensure there are no coding standard violations e.g. all boolean variables/methods sounds like booleans. Checkstyle can prevent only some coding standard violations; others need to be checked manually.
-
Ensure SLAP is applied at a reasonable level. Long methods or deeply-nested code are symptoms of low-SLAP may be counted against your code quality.
-
Reduce code duplications i.e. if there multiple blocks of code that vary only in minor ways, try to extract out similarities into one place, especially in test code.
-
In addition, try to apply as many of the
code quality guidelines covered in the module as much as you can.
Code Quality
Introduction
Basic
Can explain the importance of code quality
Always code as if the person who ends up maintaining your code will be a violent psychopath who knows where you live. -- Martin Golding
Guideline: Maximise Readability
Introduction
Can explain the importance of readability
Programs should be written and polished until they acquire publication quality. --Niklaus Wirth
Among various dimensions of code quality, such as run-time efficiency, security, and robustness, one of the most important is understandability. This is because in any non-trivial software project, code needs to be read, understood, and modified by other developers later on. Even if we do not intend to pass the code to someone else, code quality is still important because we all become 'strangers' to our own code someday.
The two code samples given below achieve the same functionality, but one is easier to read.
|
Bad |
|
Good |
|
Bad |
|
Good |
Basic
Avoid Long Methods
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid long methods
Be wary when a method is longer than the computer screen, and take corrective action when it goes beyond 30 LOC (lines of code). The bigger the haystack, the harder it is to find a needle.
Avoid Deep Nesting
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid deep nesting
If you need more than 3 levels of indentation, you're screwed anyway, and should fix your program. --Linux 1.3.53 CodingStyle
In particular, avoid arrowhead style code.
Example:

Avoid Complicated Expressions
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid complicated expressions
Avoid complicated expressions, especially those having many negations and nested parentheses. If you must evaluate complicated expressions, have it done in steps (i.e. calculate some intermediate values first and use them to calculate the final value).
Example:
Bad
return ((length < MAX_LENGTH) || (previousSize != length)) && (typeCode == URGENT);
Good
boolean isWithinSizeLimit = length < MAX_LENGTH;
boolean isSameSize = previousSize != length;
boolean isValidCode = isWithinSizeLimit || isSameSize;
boolean isUrgent = typeCode == URGENT;
return isValidCode && isUrgent;
Example:
Bad
return ((length < MAX_LENGTH) or (previous_size != length)) and (type_code == URGENT)
Good
is_within_size_limit = length < MAX_LENGTH
is_same_size = previous_size != length
is_valid_code = is_within_size_limit or is_same_size
is_urgent = type_code == URGENT
return is_valid_code and is_urgent
The competent programmer is fully aware of the strictly limited size of his own skull; therefore he approaches the programming task in full humility, and among other things he avoids clever tricks like the plague. -- Edsger Dijkstra
Avoid Magic Numbers
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid magic numbers
When the code has a number that does not explain the meaning of the number, we call that a magic number (as in “the number appears as if by magic”). Using a
Example:
|
Bad |
|
Good |
Note: Python does not have a way to make a variable a constant. However, you can use a normal variable with an ALL_CAPS name to simulate a constant.
|
Bad |
|
Good |
Similarly, we can have ‘magic’ values of other data types.
Bad
"Error 1432" // A magic string!
Make the Code Obvious
Can improve code quality using technique: make the code obvious
Make the code as explicit as possible, even if the language syntax allows them to be implicit. Here are some examples:
- [
Java] Use explicit type conversion instead of implicit type conversion. - [
Java,Python] Use parentheses/braces to show grouping even when they can be skipped. - [
Java,Python] Useenumerations when a certain variable can take only a small number of finite values. For example, instead of declaring the variable 'state' as an integer and using values 0,1,2 to denote the states 'starting', 'enabled', and 'disabled' respectively, declare 'state' as typeSystemStateand define an enumerationSystemStatethat has values'STARTING','ENABLED', and'DISABLED'.
Intermediate
Structure Code Logically
Can improve code quality using technique: structure code logically
Lay out the code so that it adheres to the logical structure. The code should read like a story. Just like we use section breaks, chapters and paragraphs to organize a story, use classes, methods, indentation and line spacing in your code to group related segments of the code. For example, you can use blank lines to group related statements together. Sometimes, the correctness of your code does not depend on the order in which you perform certain intermediary steps. Nevertheless, this order may affect the clarity of the story you are trying to tell. Choose the order that makes the story most readable.
Do Not 'Trip Up' Reader
Can improve code quality using technique: do not 'trip up' reader
Avoid things that would make the reader go ‘huh?’, such as,
- unused parameters in the method signature
- similar things look different
- different things that look similar
- multiple statements in the same line
- data flow anomalies such as, pre-assigning values to variables and modifying it without any use of the pre-assigned value
Practice KISSing
Can improve code quality using technique: practice kissing
As the old adage goes, "keep it simple, stupid” (KISS). Do not try to write ‘clever’ code. For example, do not dismiss the brute-force yet simple solution in favor of a complicated one because of some ‘supposed benefits’ such as 'better reusability' unless you have a strong justification.
Debugging is twice as hard as writing the code in the first place. Therefore, if you write the code as cleverly as possible, you are, by definition, not smart enough to debug it. --Brian W. Kernighan
Programs must be written for people to read, and only incidentally for machines to execute. --Abelson and Sussman
Avoid Premature Optimizations
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid premature optimizations
Optimizing code prematurely has several drawbacks:
- We may not know which parts are the real performance bottlenecks. This is especially the case when the code undergoes transformations (e.g. compiling, minifying, transpiling, etc.) before it becomes an executable. Ideally, you should use a profiler tool to identify the actual bottlenecks of the code first, and optimize only those parts.
- Optimizing can complicate the code, affecting correctness and understandability
- Hand-optimized code can be harder for the compiler to optimize (the simpler the code, the easier for the compiler to optimize it). In many cases a compiler can do a better job of optimizing the runtime code if you don't get in the way by trying to hand-optimize the source code.
A popular saying in the industry is make it work, make it right, make it fast which means in most cases getting the code to perform correctly should take priority over optimizing it. If the code doesn't work correctly, it has no value on matter how fast/efficient it it.
Premature optimization is the root of all evil in programming. --Donald Knuth
Note that there are cases where optimizing takes priority over other things e.g. when writing code for resource-constrained environments. This guideline simply a caution that you should optimize only when it is really needed.
SLAP Hard
Can improve code quality using technique: SLAP hard
Avoid varying the level of
Example:
Bad
readData();
salary = basic*rise+1000;
tax = (taxable?salary*0.07:0);
displayResult();
Good
readData();
processData();
displayResult();
Design → Design Fundamentals → Abstraction →
What
Abstraction is a technique for dealing with complexity. It works by establishing a level of complexity (or an aspect) we are interested in, and suppressing the more complex details below that level (or irrelevant to that aspect).
Most programs are written to solve complex problems involving large amounts of intricate details. It is impossible to deal with all these details at the same time. The guiding principle of abstraction stipulates that we capture only details that are relevant to the current perspective or the task at hand.
Ignoring lower level data items and thinking in terms of bigger entities is called data abstraction.
Within a certain software component, we might deal with a user data type, while ignoring the details contained in the user data item such as name, and date of birth. These details have been ‘abstracted away’ as they do not affect the task of that software component.
Control abstraction abstracts away details of the actual control flow to focus on tasks at a simplified level.
print(“Hello”) is an abstraction of the actual output mechanism within the computer.
Abstraction can be applied repeatedly to obtain progressively higher levels of abstractions.
An example of different levels of data abstraction: a File is a data item that is at a higher level than an array and an array is at a higher
level than a bit.
An example of different levels of control abstraction: execute(Game) is at a higher level than print(Char) which is at a higher than
an Assembly language instruction MOV.
Advanced
Make the Happy Path Prominent
Can improve code quality using technique: make the happy path prominent
The happy path (i.e. the execution path taken when everything goes well) should be clear and prominent in your code. Restructure the code to make the happy path unindented as much as possible. It is the ‘unusual’ cases that should be indented. Someone reading the code should not get distracted by alternative paths taken when error conditions happen. One technique that could help in this regard is the use of guard clauses.
Example:
Bad
if (!isUnusualCase) { //detecting an unusual condition
if (!isErrorCase) {
start(); //main path
process();
cleanup();
exit();
} else {
handleError();
}
} else {
handleUnusualCase(); //handling that unusual condition
}
In the code above,
- Unusual condition detection is separated from their handling.
- Main path is nested deeply.
Good
if (isUnusualCase) { //Guard Clause
handleUnusualCase();
return;
}
if (isErrorCase) { //Guard Clause
handleError();
return;
}
start();
process();
cleanup();
exit();
In contrast, the above code
- deals with unusual conditions as soon as they are detected so that the reader doesn't have to remember them for long.
- keeps the main path un-indented.
Guideline: Follow a Standard
Introduction
Can explain the need for following a standard
One essential way to improve code quality is to follow a consistent style. That is why software engineers follow a strict coding standard (aka style guide).
The aim of a coding standard is to make the entire code base look like it was written by one person. A coding standard is usually specific to a programming language and specifies guidelines such as the location of opening and closing braces, indentation styles and naming styles (e.g. whether to use Hungarian style, Pascal casing, Camel casing, etc.). It is important that the whole team/company use the same coding standard and that standard is not generally inconsistent with typical industry practices. If a company's coding standards is very different from what is used typically in the industry, new recruits will take longer to get used to the company's coding style.
💡 IDEs can help to enforce some parts of a coding standard e.g. indentation rules.
What is the recommended approach regarding coding standards?
c
What is the aim of using a coding standard? How does it help?
Basic
Can follow simple mechanical style rules
Learn basic guidelines of the Java coding standard (by OSS-Generic)
Sample coding standard: PEP 8 Python Style Guide -- by Python.org
Consider the code given below:
import java.util.*;
public class Task {
public static final String descriptionPrefix = "description: ";
private String description;
private boolean important;
List<String> pastDescription = new ArrayList<>(); // a list of past descriptions
public Task(String d) {
this.description = d;
if (!d.isEmpty())
this.important = true;
}
public String getAsXML() { return "<task>"+description+"</task>"; }
/**
* Print the description as a string.
*/
public void printingDescription(){ System.out.println(this); }
@Override
public String toString() { return descriptionPrefix + description; }
}
In what ways the code violate the basic guidelines (i.e., those marked with one ⭐️) of the OSS-Generic Java Coding Standard given here?
Here are three:
descriptionPrefixis a constant and should be namedDESCRIPTION_PREFIX- method name
printingDescription()should be named asprintDescription() - boolean variable
importantshould be named to sound boolean e.g.,isImportant
There are many more.
Intermediate
Can follow intermediate style rules
Go through the provided Java coding standard and learn the intermediate style rules.
According to the given Java coding standard, which one of these is not a good name?
b
Explanation: checkWeight is an action. Naming variables as actions makes the code harder to follow. isWeightValid may be a better name.
Repeat the exercise in the panel below but also find violations of intermediate level guidelines.
Consider the code given below:
import java.util.*;
public class Task {
public static final String descriptionPrefix = "description: ";
private String description;
private boolean important;
List<String> pastDescription = new ArrayList<>(); // a list of past descriptions
public Task(String d) {
this.description = d;
if (!d.isEmpty())
this.important = true;
}
public String getAsXML() { return "<task>"+description+"</task>"; }
/**
* Print the description as a string.
*/
public void printingDescription(){ System.out.println(this); }
@Override
public String toString() { return descriptionPrefix + description; }
}
In what ways the code violate the basic guidelines (i.e., those marked with one ⭐️) of the OSS-Generic Java Coding Standard given here?
Here are three:
descriptionPrefixis a constant and should be namedDESCRIPTION_PREFIX- method name
printingDescription()should be named asprintDescription() - boolean variable
importantshould be named to sound boolean e.g.,isImportant
There are many more.
Here's one you are more likely to miss:
* Print the description as a string.→* Prints the description as a string.
There are more.
Guideline: Name Well
Introduction
Can explain the need for good names in code
Proper naming improves the readability. It also reduces bugs caused by ambiguities regarding the intent of a variable or a method.
There are only two hard things in Computer Science: cache invalidation and naming things. -- Phil Karlton
Basic
Use Nouns for Things and Verbs for Actions
Can improve code quality using technique: use nouns for things and verbs for actions
Use nouns for classes/variables and verbs for methods/functions.
Examples:
| Name for a | Bad | Good |
|---|---|---|
| Class | CheckLimit |
LimitChecker |
| method | result() |
calculate() |
Distinguish clearly between single-valued and multivalued variables.
Examples:
Good
Person student;
ArrayList<Person> students;
Good
student = Person('Jim')
students = [Person('Jim'), Person('Alice')]
Use Standard Words
Can improve code quality using technique: use standard words
Use correct spelling in names. Avoid 'texting-style' spelling. Avoid foreign language words, slang, and names that are only meaningful within specific contexts/times e.g. terms from private jokes, a TV show currently popular in your country
Intermediate
Use Name to Explain
Can improve code quality using technique: use name to explain
A name is not just for differentiation; it should explain the named entity to the reader accurately and at a sufficient level of detail.
Examples:
| Bad | Good |
|---|---|
processInput() (what 'process'?) |
removeWhiteSpaceFromInput() |
flag |
isValidInput |
temp |
If the name has multiple words, they should be in a sensible order.
Examples:
| Bad | Good |
|---|---|
bySizeOrder() |
orderBySize() |
Imagine going to the doctor's and saying "My eye1 is swollen"! Don’t use numbers or case to distinguish names.
Examples:
| Bad | Bad | Good |
|---|---|---|
value1, value2 |
value, Value |
originalValue, finalValue |
Not Too Long, Not Too Short
Can improve code quality using technique: not too long, not too short
While it is preferable not to have lengthy names, names that are 'too short' are even worse. If you must abbreviate or use acronyms, do it consistently. Explain their full meaning at an obvious location.
Avoid Misleading Names
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid misleading names
Related things should be named similarly, while unrelated things should NOT.
Example: Consider these variables
colorBlack: hex value for color blackcolorWhite: hex value for color whitecolorBlue: number of times blue is usedhexForRed: : hex value for color red
This is misleading because colorBlue is named similar to colorWhite and colorBlack but has a different purpose while hexForRed is named differently
but has very similar purpose to the first two variables. The following is better:
hexForBlackhexForWhitehexForRedblueColorCount
Avoid misleading or ambiguous names (e.g. those with multiple meanings), similar sounding names, hard-to-pronounce ones (e.g. avoid ambiguities like "is that a lowercase L, capital I or number 1?", or "is that number 0 or letter O?"), almost similar names.
Examples:
| Bad | Good | Reason |
|---|---|---|
phase0 |
phaseZero |
Is that zero or letter O? |
rwrLgtDirn |
rowerLegitDirection |
Hard to pronounce |
right left wrong |
rightDirection leftDirection wrongResponse |
right is for 'correct' or 'opposite of 'left'? |
redBooks readBooks |
redColorBooks booksRead |
red and read (past tense) sounds the same |
FiletMignon |
egg |
If the requirement is just a name of a food, egg is a much easier to type/say choice than FiletMignon |
Guideline: Avoid Unsafe Shortcuts
Introduction
Can explain the need for avoiding error-prone shortcuts
It is safer to use language constructs in the way they are meant to be used, even if the language allows shortcuts. Some such coding practices are common sources of bugs. Know them and avoid them.
Basic
Use the Default Branch
Can improve code quality using technique: use the default branch
Always include a default branch in case statements.
Furthermore, use it for the intended default action and not just to execute the last option. If there is no default action, you can use the 'default' branch to detect errors (i.e. if execution reached
the default branch, throw an exception). This also applies to the final else of an if-else construct. That is, the final else should mean 'everything
else', and not the final option. Do not use else when an if condition can be explicitly specified, unless there is absolutely no other possibility.
Bad
if (red) print "red";
else print "blue";
Good
if (red) print "red";
else if (blue) print "blue";
else error("incorrect input");
Don't Recycle Variables or Parameters
Can improve code quality using technique: don't recycle variables or parameters
- Use one variable for one purpose. Do not reuse a variable for a different purpose other than its intended one, just because the data type is the same.
- Do not reuse formal parameters as local variables inside the method.
Bad
double computeRectangleArea(double length, double width) {
length = length * width;
return length;
}
Good
double computeRectangleArea(double length, double width) {
double area;
area = length * width;
return area;
}
Avoid Empty Catch Blocks
Can improve code quality using technique: avoid empty catch blocks
Never write an empty catch statement. At least give a comment to explain why the catch block is left empty.
Delete Dead Code
Can improve code quality using technique: delete dead code
We all feel reluctant to delete code we have painstakingly written, even if we have no use for that code any more ("I spent a lot of time writing that code; what if we need it again?"). Consider all code as baggage you have to carry; get rid of unused code the moment it becomes redundant. If you need that code again, simply recover it from the revision control tool you are using. Deleting code you wrote previously is a sign that you are improving.
Intermediate
Minimise Scope of Variables
Can improve code quality using technique: minimise scope of variables
Minimize global variables. Global variables may be the most convenient way to pass information around, but they do create implicit links between code segments that use the global variable. Avoid them as much as possible.
Define variables in the least possible scope. For example, if the variable is used only within the if block of the conditional statement, it should be declared inside that
if block.
The most powerful technique for minimizing the scope of a local variable is to declare it where it is first used. -- Effective Java, by Joshua Bloch
Resources:
Minimise Code Duplication
Can improve code quality using technique: minimise code duplication
Code duplication, especially when you copy-paste-modify code, often indicates a poor quality implementation. While it may not be possible to have zero duplication, always think twice before duplicating code; most often there is a better alternative.
This guideline is closely related to the
Supplmentary → Principles →
DRY Principle
DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) Principle: Every piece of knowledge must have a single, unambiguous, authoritative representation within a system The Pragmatic Programmer, by Andy Hunt and Dave Thomas
This principle guards against duplication of information.
The functionality implemented twice is a violation of the DRY principle even if the two implementations are different.
The value a system-wide timeout being defined in multiple places is a violation of DRY.
Guideline: Comment Minimally, but Sufficiently
Introduction
Can explain the need for commenting minimally but sufficiently
Good code is its own best documentation. As you’re about to add a comment, ask yourself, ‘How can I improve the code so that this comment isn’t needed?’ Improve the code and then document it to make it even clearer. --Steve McConnell, Author of Clean Code
Some think commenting heavily increases the 'code quality'. This is not so. Avoid writing comments to explain bad code. Improve the code to make it self-explanatory.
Basic
Do Not Repeat the Obvious
Can improve code quality using technique: do not repeat the obvious
If the code is self-explanatory, refrain from repeating the description in a comment just for the sake of 'good documentation'.
Bad
// increment x
x++;
//trim the input
trimInput();
Write to the Reader
Can improve code quality using technique: write to the reader
Do not write comments as if they are private notes to self. Instead, write them well enough to be understood by another programmer. One type of comments that is almost always useful is the header comment that you write for a class or an operation to explain its purpose.
Examples:
Bad Reason: this comment will only make sense to the person who wrote it
// a quick trim function used to fix bug I detected overnight
void trimInput(){
....
}
Good
/** Trims the input of leading and trailing spaces */
void trimInput(){
....
}
Bad Reason: this comment will only make sense to the person who wrote it
# a quick trim function used to fix bug I detected overnight
def trim_input():
...
Good
def trim_input():
"""Trim the input of leading and trailing spaces"""
...
Intermediate
Explain WHAT and WHY, not HOW
Can improve code quality using technique: explain what and why, not how
Comments should explain what and why aspect of the code, rather than the how aspect.
👍 What : The specification of what the code supposed to do. The reader can compare such comments to the implementation to verify if the implementation is correct
Example: This method is possibly buggy because the implementation does not seem to match the comment. In this case the comment could help the reader to detect the bug.
/** Removes all spaces from the {@code input} */
void compact(String input){
input.trim();
}
👍 Why : The rationale for the current implementation.
Example: Without this comment, the reader will not know the reason for calling this method.
// Remove spaces to comply with IE23.5 formatting rules
compact(input);
👎 How : The explanation for how the code works. This should already be apparent from the code, if the code is self-explanatory. Adding comments to explain the same thing is redundant.
Example:
Bad Reason: Comment explains how the code works.
// return true if both left end and right end are correct or the size has not incremented
return (left && right) || (input.size() == size);
Good Reason: Code refactored to be self-explanatory. Comment no longer needed.
boolean isSameSize = (input.size() == size) ;
return (isLeftEndCorrect && isRightEndCorrect) || isSameSize;
null
B. Depth and completeness of the major feature
Evaluates: How good is your Quality Assurance?
Based on: 1. your test code 2. our own manual testing 3. your performance in the two Practical Exams (PE), 4. bugs found during PE.
Relevant: [
What: The v1.3 is subjected to a round of peer acceptance/system testing, also called the Practical Exam Round 1 (PE-1). This round of testing will be graded similar to the
When, where: 45 minute slot at the end of week 11 lecture, in the Lecture venue
Objectives:
- Evaluate your,
- manual testing skills
- product evaluation skills
- effort estimation skills
- Peer-evaluate your
- product design
- implementation effort
- documentation quality
When, where: Week 13 lecture
Grading:
- Your performance in the practical exams will be considered for your final grade (under the QA category and under Implementation category, about 10 marks in total).
- You will be graded based on your effectiveness as a tester (e.g., the percentage of the bugs you found, the nature of the bugs you found) and how far off your evaluation/estimates are from the evaluator consensus. Explanation: we understand that you have limited expertise in this area; hence, we penalize only if your inputs don't seem to be based on a sincere effort to test/evaluate.
- The bugs found in your product by others will affect your v1.4 marks. You will be given a chance to reject false-positive bug reports.
Preparation:
-
Ensure that you can access the relevant issue tracker given below:
-- for PE-1: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1
-- for PE-2: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2- These are private repos!. If you cannot access the relevant repo, you may not have accepted the invitation to join the GitHub org used by the module. Go to https://github.com/orgs/nusCS2113-AY1819S1/invitation to accept the invitation.
- If you cannot find the invitation, post in our forum.
-
Ensure you have access to a computer that is able to run module projects e.g. has the right Java version.
-
Have a good screen grab tool with annotation features so that you can quickly take a screenshot of a bug, annotate it, and post in the issue tracker.
- 💡 You can use Ctrl+V to paste a picture from the clipboard into a text box in GitHub issue tracker.
-
Charge your computer before coming to the PE session. The testing venue may not have enough charging points.
During:
- Take note of your team to test. It will be given to you by the teaching team (distributed via IVLE gradebook).
- Download from IVLE all files submitted by the team (i.e. jar file, User Guide, Developer Guide, and Project Portfolio Pages) into an empty folder.
- [~45 minutes] Test the product and report bugs as described below:
Testing instructions for PE-1 and PE-2
-
What to test:
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
helpcommand). - Do system testing first i.e., does the product work as specified by the documentation?. If there is time left, you can do acceptance testing as well i.e., does the product solve the problem it claims to solve?.
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
- PE-2 (at v1.4):
- Test the product based on the Developer Guide (Appendix named Instructions for Manual Testing) and the User Guide. The testing instructions in the Developer Guide can provide you some guidance but if you follow those instructions strictly, you are unlikely to find many bugs. You can deviate from the instructions to probe areas that are more likely to have bugs.
- Do system testing only i.e., verify actual behavior against documented behavior. Do not do acceptance testing.
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
-
What not to test:
- Omit features that are driven by GUI inputs (e.g. buttons, menus, etc.) Reason: Only CLI-driven features can earn credit, as per given project constraints. Some features might have both a GUI-driven and CLI-driven ways to invoke them, in which case test only the CLI-driven way of invoking it.
- Omit feature that existed in AB-4.
-
These are considered bugs:
- Behavior differs from the User Guide
- A legitimate user behavior is not handled e.g. incorrect commands, extra parameters
- Behavior is not specified and differs from normal expectations e.g. error message does not match the error
- Problems in the User Guide e.g., missing/incorrect info
-
Where to report bugs: Post bug in the following issue trackers (not in the team's repo):
- PE-1 (at v1.3): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2.
-
Bug report format:
- Post bugs as you find them (i.e., do not wait to post all bugs at the end) because the issue tracker will close exactly at the end of the allocated time.
- Do not use team ID in bug reports. Reason: to prevent others copying your bug reports
- Each bug should be a separate issue.
- Write good quality bug reports; poor quality or incorrect bug reports will not earn credit.
- Use a descriptive title.
- Give a good description of the bug with steps to reproduce and screenshots.
- Use the template(s) in the issue tracker as much as possible.
- Assign a severity to the bug report. Bug report without a priority label are considered
severity.Low(lower severity bugs earn lower credit):
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
About posting suggestions:
- PE-1 (at v1.3): You can also post suggestions on how to improve the product. 💡 Be diplomatic when reporting bugs or suggesting improvements. For example, instead of criticising the current behavior, simply suggest alternatives to consider.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): Do not post suggestions.
-
If the product doesn't work at all: If the product fails catastrophically e.g., cannot even launch, contact the lecturer immediately to obtain a new product to test.
-
[~45 minutes] Evaluate the following aspects. Note down your evaluation in a hard copy (as a backup). Submit via TEAMMATES.
-
A. Cohesiveness of product features []: Do the features fit together and match the stated target user and the value proposition?
unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: One of these- target user is too general i.e. wider than AB4
- target user and/or value proposition is not clear from the user guide
- features don't seem to fit together for the most part
medium: Some features fit together but some don't.high: All features fit together but the features are not very high value to the target user.excellent: The target user is clearly defined (not too general) and almost all new features are of high-value to the target user. i.e. the product is very attractive to the target user.
-
B. Quality of user docs []: Evaluate based on the parts of the user guide written by the person, as reproduced in the project portfolio. Evaluate from an end-user perspective.
unable to judge: Less than 1 page worth of UG content written by the student.low: Hard to understand, often inaccurate or missing important information.medium: Needs some effort to understand; some information is missing.high: Mostly easy to follow. Only a few areas need improvements.excellent: Easy to follow and accurate. Just enough information, visuals, examples etc. (not too much either).
-
C. Quality of developer docs []: Evaluate based on the developer docs cited/reproduced in the respective project portfolio page. Evaluate from the perspective of a new developer trying to understand how the features are implemented.
unable to judge: One of these- no content at all.
- less than 0.5 pages worth of content.
- other problems in the document e.g. looks like included wrong content.
low: One of these- Very small amount of content (i.e., 0.5 - 1 page).
- Hardly any use to the reader (i.e., content doesn't make much sense or redundant).
- Uses ad-hoc diagrams where UML diagrams could have been used instead.
- Multiple notation errors in UML diagrams.
medium: Some diagrams, some descriptions, but does not help the reader that much e.g. overly complicated diagrams.high: Enough diagrams (at lest two kinds of UML diagrams used) and enough descriptions (about 2 pages worth) but explanations are not always easy to follow.excellent: Easy to follow. Just enough information (not too much). Minimum repetition of content/diagrams. Good use of diagrams to complement text descriptions. Easy to understand diagrams with just enough details rather than very complicated diagrams that are hard to understand.
-
D. Depth of feature []: Evaluate the feature done by the student for difficulty, depth, and completeness. Note: examples given below assumes AB4 did not have the commands
edit,undo, andredo.unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: An easy feature e.g. make the existing find command case insensitive.medium: Moderately difficult feature, barely acceptable implementation e.g. an edit command that requires the user to type all fields, even the ones that are not being edited.high: One of the below- A moderately difficult feature but fully implemented e.g. an edit command that allows editing any field.
- A difficult feature with a reasonable implementation but some aspects are not covered undo/redo command that only allows a single undo/redo.
excellent: A difficult feature, all reasonable aspects are fully implemented undo/redo command that allows multiple undo/redo.
-
E. Amount of work []: Evaluate the amount of work, on a scale of 0 to 30.
- Consider this PR (
historycommand) as 5 units of effort which means this PR (undo/redocommand) is about 15 points of effort. Given that 30 points matches an effort twice as that needed for theundo/redofeature (which was given as an example of anAgrade project), we expect most students to be have efforts lower than 20. - Consider the main feature only. Exclude GUI inputs, but consider GUI outputs of the feature. Count all implementation/testing/documentation work as mentioned in that person's portfolio page. Also look at the actual code written by the person. We understand that it is not possible to know exactly which part of the code is for the main feature; make a best guess judgement call based on the available info.
- Do not give a high value just to be nice. If your estimate is wildly inaccurate, it means you are unable to estimate the effort required to implement a feature in a project that you are supposed to know well at this point. You will lose marks if that is the case.
- Consider this PR (
-
Bug Review Period:
There will be a review period for you to respond to the bug reports you received.
Duration: The review period will start around 1 day after the PE (exact time to be announced) and will last until the following Tuesday midnight.
Bug reviewing is recommended to be done as a team as some of the decisions need team consensus.
Instructions for Reviewing Bug Reports
-
First, don't freak out if there are lot of bug reports. Many can be duplicates and some can be false positives. In any case, we anticipate that all of these products will have some bugs and our penalty for bugs is not harsh. Furthermore, it depends on the severity of the bug. Some bug may not even be penalized.
-
Do not edit the subject or the description. Do not close bug reports. Your response (if any) should be added as a comment.
-
If the bug is reported multiple times, mark all copies EXCEPT one as duplicates using the
duplicatetag (if the duplicates have different severity levels, you should keep the one with the highest severity). In addition, use this technique to indicate which issue they are duplicates of. Duplicates can be omitted from processing steps given below. -
If a bug seems to be for a different product (i.e. wrongly assigned to your team), let us know (email prof).
-
Decide if it is a real bug and apply ONLY one of these labels.
Response Labels:
response.Accepted: You accept it as a bug.response.Rejected: What tester thought as a bug is in fact expected behavior. ❗️ The penalty for rejecting a bug using an unjustifiable explanation is higher than the penalty if the same bug was accepted. You can also reject bugs that you inherited from AB4.response.CannotReproduce: You are unable to reproduce the behavior reported in the bug after multiple tries.response.IssueUnclear: The issue description is not clear.
- If applicable, decide the type of bug. Bugs without
type-are consideredtype-FunctionalityBugby default (which are liable to a heavier penalty):
Bug Type Labels:
type-FunctionalityBug: the bug is a flaw in how the product works.type-DocumentationBug: the bug is in the documentation.
- If you disagree with the original severity assigned to the bug, you may change it to the correct level, in which case add a comment justifying the change. All such changes will be double-checked by the teaching team and unreasonable lowering of severity will be penalized extra.:
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
Decide who should fix the bug. Use the
Assigneesfield to assign the issue to that person(s). There is no need to actually fix the bug though. It's simply an indication/acceptance of responsibility. If there is no assignee, we will distribute the penalty for that bug (if any) among all team members. -
Add an explanatory comment explaining your choice of labels and assignees.
Grading: Taking part in the PE-1 is strongly encouraged as it can affect your grade in the following ways.
- We will consider your performance in both PE-1 as well as PE-2 when grading.
- You will be graded based on your effectiveness as a tester (e.g., the percentage of the bugs you found, the nature of the bugs you found) and how far off your evaluation/estimates are from the evaluator consensus. Explanation: we understand that you have limited expertise in this area; hence, we penalize only if your inputs don't seem to be based on a sincere effort to test/evaluate.
- There is no penalty for bugs reported in your product. Every bug you find is a win-win for you and the team whose product you are testing.
Objectives:
- To train you to do manual testing, bug reporting, bug
triaging, bug fixing, communicating with users/testers/developers, evaluating products etc. - To help you improve your product before the final submission.
Preparation:
-
Ensure that you can access the relevant issue tracker given below:
-- for PE-1: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1
-- for PE-2: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2- These are private repos!. If you cannot access the relevant repo, you may not have accepted the invitation to join the GitHub org used by the module. Go to https://github.com/orgs/nusCS2113-AY1819S1/invitation to accept the invitation.
- If you cannot find the invitation, post in our forum.
-
Ensure you have access to a computer that is able to run module projects e.g. has the right Java version.
-
Have a good screen grab tool with annotation features so that you can quickly take a screenshot of a bug, annotate it, and post in the issue tracker.
- 💡 You can use Ctrl+V to paste a picture from the clipboard into a text box in GitHub issue tracker.
-
Charge your computer before coming to the PE session. The testing venue may not have enough charging points.
During the session:
- Take note of your team to test. Distributed via IVLE gradebook.
- Download the latest jar file from the team's GitHub page. Copy it to an empty folder.
Testing instructions for PE-1 and PE-2
-
What to test:
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
helpcommand). - Do system testing first i.e., does the product work as specified by the documentation?. If there is time left, you can do acceptance testing as well i.e., does the product solve the problem it claims to solve?.
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
- PE-2 (at v1.4):
- Test the product based on the Developer Guide (Appendix named Instructions for Manual Testing) and the User Guide. The testing instructions in the Developer Guide can provide you some guidance but if you follow those instructions strictly, you are unlikely to find many bugs. You can deviate from the instructions to probe areas that are more likely to have bugs.
- Do system testing only i.e., verify actual behavior against documented behavior. Do not do acceptance testing.
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
-
What not to test:
- Omit features that are driven by GUI inputs (e.g. buttons, menus, etc.) Reason: Only CLI-driven features can earn credit, as per given project constraints. Some features might have both a GUI-driven and CLI-driven ways to invoke them, in which case test only the CLI-driven way of invoking it.
- Omit feature that existed in AB-4.
-
These are considered bugs:
- Behavior differs from the User Guide
- A legitimate user behavior is not handled e.g. incorrect commands, extra parameters
- Behavior is not specified and differs from normal expectations e.g. error message does not match the error
- Problems in the User Guide e.g., missing/incorrect info
-
Where to report bugs: Post bug in the following issue trackers (not in the team's repo):
- PE-1 (at v1.3): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2.
-
Bug report format:
- Post bugs as you find them (i.e., do not wait to post all bugs at the end) because the issue tracker will close exactly at the end of the allocated time.
- Do not use team ID in bug reports. Reason: to prevent others copying your bug reports
- Each bug should be a separate issue.
- Write good quality bug reports; poor quality or incorrect bug reports will not earn credit.
- Use a descriptive title.
- Give a good description of the bug with steps to reproduce and screenshots.
- Use the template(s) in the issue tracker as much as possible.
- Assign a severity to the bug report. Bug report without a priority label are considered
severity.Low(lower severity bugs earn lower credit):
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
About posting suggestions:
- PE-1 (at v1.3): You can also post suggestions on how to improve the product. 💡 Be diplomatic when reporting bugs or suggesting improvements. For example, instead of criticising the current behavior, simply suggest alternatives to consider.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): Do not post suggestions.
-
If the product doesn't work at all: If the product fails catastrophically e.g., cannot even launch, contact the lecturer immediately to obtain a new product to test.
At the end of the project each student is required to submit a Project Portfolio Page.
-
Objective:
- For you to use (e.g. in your resume) as a well-documented data point of your SE experience
- For us to use as a data point to evaluate your,
- contributions to the project
- your documentation skills
-
Sections to include:
-
Overview: A short overview of your product to provide some context to the reader.
-
Summary of Contributions:
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
https://nuscs2113-ay1819s1.github.io/dashboard/#=undefined&search=githbub_username_in_lower_case(replacegithbub_username_in_lower_casewith your actual username in lower case e.g.,johndoe). This link is also available in the Project List Page -- linked to the icon under your photo. - Main feature implemented: A summary of the main feature you implemented
- Other contributions:
- Contributions to project management e.g., setting up project tools, managing releases, managing issue tracker etc.
- Evidence of helping others e.g. responses you posted in our forum, bugs you reported in other team's products,
- Evidence of technical leadership e.g. sharing useful information in the forum
- [Optional] Other minor enhancements: If you have other enhancements that you implemented, which are not related to your main feature, you can include it here. If you have written a significant amount of code that can be advertised as a feature by itself, but does not belong to your main feature, you can choose to include it as a part of the optional enhancements.
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on Project Code Dashboard, which should be
-
Contributions to the User Guide: Reproduce the parts in the User Guide that you wrote. This can include features you implemented as well as features you propose to implement.
The purpose of allowing you to include proposed features is to provide you more flexibility to show your documentation skills. e.g. you can bring in a proposed feature just to give you an opportunity to use a UML diagram type not used by the actual features. -
Contributions to the Developer Guide: Reproduce the parts in the Developer Guide that you wrote. Ensure there is enough content to evaluate your technical documentation skills and UML modelling skills. You can include descriptions of your design/implementations, possible alternatives, pros and cons of alternatives, etc.
-
If you plan to use the PPP in your Resume, you can also include your SE work outside of the module (will not be graded)
-
-
Format:
-
File name:
docs/team/githbub_username_in_lower_case.adoce.g.,docs/team/johndoe.adoc -
Follow the example in the AddressBook-Level4, but ignore the following two lines in it.
- Minor enhancement: added a history command that allows the user to navigate to previous commands using up/down keys.
- Code contributed: [Functional code] [Test code] {give links to collated code files}
-
💡 You can use the Asciidoc's
includefeature to include sections from the developer guide or the user guide in your PPP. Follow the example in the sample. -
It is assumed that all contents in the PPP were written primarily by you. If any section is written by someone else e.g. someone else wrote described the feature in the User Guide but you implemented the feature, clearly state that the section was written by someone else (e.g.
Start of Extract [from: User Guide] written by Jane Doe). Reason: Your writing skills will be evaluated based on the PPP -
Page limit: If you have more content than the limit given below, shorten (or omit some content) so that you do not exceed the page limit. Having too much content in the PPP will be viewed unfavorably during grading. Note: the page limits given below are after converting to PDF format. The actual amount of content you require is actually less than what these numbers suggest because the HTML → PDF conversion adds a lot of spacing around content.
Content Limit Overview + Summary of contributions 0.5-1 Contributions to the User Guide 1-3 Contributions to the Developer Guide 3-6 Total 5-10
-
After the session:
- We'll transfer the relevant bug reports to your repo over the weekend. Once you have received the bug reports for your product, it is up to you to decide whether you will act on reported issues before the final submission v1.4. For some issues, the correct decision could be to reject or postpone to a version beyond v1.4.
- You can post in the issue thread to communicate with the tester e.g. to ask for more info, etc. However, the tester is not obliged to respond.
- 💡 Do not argue with the issue reporter to try to convince that person that your way is correct/better. If at all, you can gently explain the rationale for the current behavior but do not waste time getting involved in long arguments. If you think the suggestion/bug is unreasonable, just thank the reporter for their view and close the issue.
Relevant: [
Objectives:
- Evaluate your,
- manual testing skills
- product evaluation skills
- effort estimation skills
- Peer-evaluate your
- product design
- implementation effort
- documentation quality
When, where: Week 13 lecture
Grading:
- Your performance in the practical exams will be considered for your final grade (under the QA category and under Implementation category, about 10 marks in total).
- You will be graded based on your effectiveness as a tester (e.g., the percentage of the bugs you found, the nature of the bugs you found) and how far off your evaluation/estimates are from the evaluator consensus. Explanation: we understand that you have limited expertise in this area; hence, we penalize only if your inputs don't seem to be based on a sincere effort to test/evaluate.
- The bugs found in your product by others will affect your v1.4 marks. You will be given a chance to reject false-positive bug reports.
Preparation:
-
Ensure that you can access the relevant issue tracker given below:
-- for PE-1: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1
-- for PE-2: nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2- These are private repos!. If you cannot access the relevant repo, you may not have accepted the invitation to join the GitHub org used by the module. Go to https://github.com/orgs/nusCS2113-AY1819S1/invitation to accept the invitation.
- If you cannot find the invitation, post in our forum.
-
Ensure you have access to a computer that is able to run module projects e.g. has the right Java version.
-
Have a good screen grab tool with annotation features so that you can quickly take a screenshot of a bug, annotate it, and post in the issue tracker.
- 💡 You can use Ctrl+V to paste a picture from the clipboard into a text box in GitHub issue tracker.
-
Charge your computer before coming to the PE session. The testing venue may not have enough charging points.
During:
- Take note of your team to test. It will be given to you by the teaching team (distributed via IVLE gradebook).
- Download from IVLE all files submitted by the team (i.e. jar file, User Guide, Developer Guide, and Project Portfolio Pages) into an empty folder.
- [~45 minutes] Test the product and report bugs as described below:
Testing instructions for PE-1 and PE-2
-
What to test:
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
helpcommand). - Do system testing first i.e., does the product work as specified by the documentation?. If there is time left, you can do acceptance testing as well i.e., does the product solve the problem it claims to solve?.
- Test the product based on the User Guide (the UG is most likely accessible using the
- PE-2 (at v1.4):
- Test the product based on the Developer Guide (Appendix named Instructions for Manual Testing) and the User Guide. The testing instructions in the Developer Guide can provide you some guidance but if you follow those instructions strictly, you are unlikely to find many bugs. You can deviate from the instructions to probe areas that are more likely to have bugs.
- Do system testing only i.e., verify actual behavior against documented behavior. Do not do acceptance testing.
- PE-1 (at v1.3):
-
What not to test:
- Omit features that are driven by GUI inputs (e.g. buttons, menus, etc.) Reason: Only CLI-driven features can earn credit, as per given project constraints. Some features might have both a GUI-driven and CLI-driven ways to invoke them, in which case test only the CLI-driven way of invoking it.
- Omit feature that existed in AB-4.
-
These are considered bugs:
- Behavior differs from the User Guide
- A legitimate user behavior is not handled e.g. incorrect commands, extra parameters
- Behavior is not specified and differs from normal expectations e.g. error message does not match the error
- Problems in the User Guide e.g., missing/incorrect info
-
Where to report bugs: Post bug in the following issue trackers (not in the team's repo):
- PE-1 (at v1.3): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-1.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): nusCS2113-AY1819S1/pe-2.
-
Bug report format:
- Post bugs as you find them (i.e., do not wait to post all bugs at the end) because the issue tracker will close exactly at the end of the allocated time.
- Do not use team ID in bug reports. Reason: to prevent others copying your bug reports
- Each bug should be a separate issue.
- Write good quality bug reports; poor quality or incorrect bug reports will not earn credit.
- Use a descriptive title.
- Give a good description of the bug with steps to reproduce and screenshots.
- Use the template(s) in the issue tracker as much as possible.
- Assign a severity to the bug report. Bug report without a priority label are considered
severity.Low(lower severity bugs earn lower credit):
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
About posting suggestions:
- PE-1 (at v1.3): You can also post suggestions on how to improve the product. 💡 Be diplomatic when reporting bugs or suggesting improvements. For example, instead of criticising the current behavior, simply suggest alternatives to consider.
- PE-2 (at v1.4): Do not post suggestions.
-
If the product doesn't work at all: If the product fails catastrophically e.g., cannot even launch, contact the lecturer immediately to obtain a new product to test.
-
[~45 minutes] Evaluate the following aspects. Note down your evaluation in a hard copy (as a backup). Submit via TEAMMATES.
-
A. Cohesiveness of product features []: Do the features fit together and match the stated target user and the value proposition?
unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: One of these- target user is too general i.e. wider than AB4
- target user and/or value proposition is not clear from the user guide
- features don't seem to fit together for the most part
medium: Some features fit together but some don't.high: All features fit together but the features are not very high value to the target user.excellent: The target user is clearly defined (not too general) and almost all new features are of high-value to the target user. i.e. the product is very attractive to the target user.
-
B. Quality of user docs []: Evaluate based on the parts of the user guide written by the person, as reproduced in the project portfolio. Evaluate from an end-user perspective.
unable to judge: Less than 1 page worth of UG content written by the student.low: Hard to understand, often inaccurate or missing important information.medium: Needs some effort to understand; some information is missing.high: Mostly easy to follow. Only a few areas need improvements.excellent: Easy to follow and accurate. Just enough information, visuals, examples etc. (not too much either).
-
C. Quality of developer docs []: Evaluate based on the developer docs cited/reproduced in the respective project portfolio page. Evaluate from the perspective of a new developer trying to understand how the features are implemented.
unable to judge: One of these- no content at all.
- less than 0.5 pages worth of content.
- other problems in the document e.g. looks like included wrong content.
low: One of these- Very small amount of content (i.e., 0.5 - 1 page).
- Hardly any use to the reader (i.e., content doesn't make much sense or redundant).
- Uses ad-hoc diagrams where UML diagrams could have been used instead.
- Multiple notation errors in UML diagrams.
medium: Some diagrams, some descriptions, but does not help the reader that much e.g. overly complicated diagrams.high: Enough diagrams (at lest two kinds of UML diagrams used) and enough descriptions (about 2 pages worth) but explanations are not always easy to follow.excellent: Easy to follow. Just enough information (not too much). Minimum repetition of content/diagrams. Good use of diagrams to complement text descriptions. Easy to understand diagrams with just enough details rather than very complicated diagrams that are hard to understand.
-
D. Depth of feature []: Evaluate the feature done by the student for difficulty, depth, and completeness. Note: examples given below assumes AB4 did not have the commands
edit,undo, andredo.unable to judge: You are unable to judge this aspect for some reason.low: An easy feature e.g. make the existing find command case insensitive.medium: Moderately difficult feature, barely acceptable implementation e.g. an edit command that requires the user to type all fields, even the ones that are not being edited.high: One of the below- A moderately difficult feature but fully implemented e.g. an edit command that allows editing any field.
- A difficult feature with a reasonable implementation but some aspects are not covered undo/redo command that only allows a single undo/redo.
excellent: A difficult feature, all reasonable aspects are fully implemented undo/redo command that allows multiple undo/redo.
-
E. Amount of work []: Evaluate the amount of work, on a scale of 0 to 30.
- Consider this PR (
historycommand) as 5 units of effort which means this PR (undo/redocommand) is about 15 points of effort. Given that 30 points matches an effort twice as that needed for theundo/redofeature (which was given as an example of anAgrade project), we expect most students to be have efforts lower than 20. - Consider the main feature only. Exclude GUI inputs, but consider GUI outputs of the feature. Count all implementation/testing/documentation work as mentioned in that person's portfolio page. Also look at the actual code written by the person. We understand that it is not possible to know exactly which part of the code is for the main feature; make a best guess judgement call based on the available info.
- Do not give a high value just to be nice. If your estimate is wildly inaccurate, it means you are unable to estimate the effort required to implement a feature in a project that you are supposed to know well at this point. You will lose marks if that is the case.
- Consider this PR (
-
Bug Review Period:
There will be a review period for you to respond to the bug reports you received.
Duration: The review period will start around 1 day after the PE (exact time to be announced) and will last until the following Tuesday midnight.
Bug reviewing is recommended to be done as a team as some of the decisions need team consensus.
Instructions for Reviewing Bug Reports
-
First, don't freak out if there are lot of bug reports. Many can be duplicates and some can be false positives. In any case, we anticipate that all of these products will have some bugs and our penalty for bugs is not harsh. Furthermore, it depends on the severity of the bug. Some bug may not even be penalized.
-
Do not edit the subject or the description. Do not close bug reports. Your response (if any) should be added as a comment.
-
If the bug is reported multiple times, mark all copies EXCEPT one as duplicates using the
duplicatetag (if the duplicates have different severity levels, you should keep the one with the highest severity). In addition, use this technique to indicate which issue they are duplicates of. Duplicates can be omitted from processing steps given below. -
If a bug seems to be for a different product (i.e. wrongly assigned to your team), let us know (email prof).
-
Decide if it is a real bug and apply ONLY one of these labels.
Response Labels:
response.Accepted: You accept it as a bug.response.Rejected: What tester thought as a bug is in fact expected behavior. ❗️ The penalty for rejecting a bug using an unjustifiable explanation is higher than the penalty if the same bug was accepted. You can also reject bugs that you inherited from AB4.response.CannotReproduce: You are unable to reproduce the behavior reported in the bug after multiple tries.response.IssueUnclear: The issue description is not clear.
- If applicable, decide the type of bug. Bugs without
type-are consideredtype-FunctionalityBugby default (which are liable to a heavier penalty):
Bug Type Labels:
type-FunctionalityBug: the bug is a flaw in how the product works.type-DocumentationBug: the bug is in the documentation.
- If you disagree with the original severity assigned to the bug, you may change it to the correct level, in which case add a comment justifying the change. All such changes will be double-checked by the teaching team and unreasonable lowering of severity will be penalized extra.:
Bug Severity labels:
severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
-
Decide who should fix the bug. Use the
Assigneesfield to assign the issue to that person(s). There is no need to actually fix the bug though. It's simply an indication/acceptance of responsibility. If there is no assignee, we will distribute the penalty for that bug (if any) among all team members. -
Add an explanatory comment explaining your choice of labels and assignees.
- There is no requirement for a minimum coverage level. Note that in a production environment you are often required to have at least 90% of the code covered by tests. In this project, it can be less. The less coverage you have, the higher the risk of regression bugs, which will cost marks if not fixed before the final submission.
- You must write some tests so that we can evaluate your ability to write tests.
- How much of each type of testing should you do? We expect you to decide. You learned different types of testing and what they try to achieve. Based on that, you should decide how much of each type is required. Similarly, you can decide to what extent you want to automate tests, depending on the benefits and the effort required.
- Applying TDD is optional. If you plan to test something, it is better to apply TDD because TDD ensures that you write functional code in a testable way. If you do it the normal way, you often find that it is hard to test the functional code because the code has low testability.
Evaluates: How well does your user guide achieves its objectives?
Based on: the relevant sections of your project portfolio. Criteria considered:
- Explanation should be clear and written to match the audience.
- Good use of visuals to complement text.
A. Process:
Evaluates: How well you did in project management related aspects of the project, as an individual and as a team
Based on: Supervisor observations of project milestones and GitHub data.
Milestones need to be reached the midnight before of the tutorial for it to be counted as achieved. To get a good grade this aspect, achieve recommended weekly progress in at least 6/10 weeks.
Other criteria:
- Good use of GitHub milestones
- Good use of GitHub release mechanism
- Good version control, based on the repo
- Reasonable attempt to use the forking workflow
- Good task definition, assignment and tracking, based on the issue tracker
- Good use of buffers (opposite: everything at the last minute)
- Project done iteratively and incrementally (opposite: doing most of the work in one big burst)
B. Team-based tasks:
Evaluates: How much you contributed to common team-based tasks
Based on: peer evaluations and tutor observations
Relevant: [
Here is a non-exhaustive list of team-tasks:
- Necessary general code enhancements e.g.,
- Work related to renaming the product
- Work related to changing the product icon
- Morphing the product into a different product
- Setting up the GitHub, Travis, AppVeyor, etc.,
- Maintaining the issue tracker
- Release management
- Updating user/developer docs that are not specific to a feature e.g. documenting the target user profile
- Incorporating more useful tools/libraries/frameworks into the product or the project workflow (e.g. automate more aspects of the project workflow using a GitHub plugin)
10 marks allocated for participation can be earned in the following ways (there are ~28 available marks to choose from):
-
Good peer ratings - Criteria for professional conduct (1 mark for each criterion, max 7)
- Competency criteria (2 marks for each, max 6)
- In-lecture quizzes
- In-lecture quizzes, roughly two questions each week (0.5 each, max 10 marks)
- Module admin tasks done on time and as instructed
- Peer evaluations (1 mark each)
- Pre-module survey (1 mark)
- Enhanced AB1-AB3: 2 mark each
Relevant: [
Peer evaluation criteria: professional conduct
- Professional Communication :
- Communicates sufficiently and professionally. e.g. Does not use offensive language or excessive slang in project communications.
- Responds to communication from team members in a timely manner (e.g. within 24 hours).
- Punctuality: Does not cause others to waste time or slow down project progress by frequent tardiness.
- Dependability: Promises what can be done, and delivers what was promised.
- Effort: Puts in sufficient effort to, and tries their best to keep up with the module/project pace. Seeks help from others when necessary.
- Quality: Does not deliver work products that seem to be below the student's competence level i.e. tries their best to make the work product as high quality as possible within her competency level.
- Meticulousness:
- Rarely overlooks submission requirements.
- Rarely misses compulsory module activities such as completing the TEAMMATES profile or peer review.
- Teamwork: How willing are you to act as part of a team, contribute to team-level tasks, adhere to team decisions, etc.
Peer evaluation criteria: competency
- Technical Competency: Able to gain competency in all the required tools and techniques.
- Mentoring skills: Helps others when possible. Able to mentor others well.
- Communication skills: Able to communicate (written and spoken) well. Takes initiative in discussions.
Your tutor will serve as your project supervisor too.
The supervisor's main job is to observe, facilitate self/peer learning, evaluate, and give feedback.
Tutorial time is the main avenue for meeting your supervisor. In addition, you can meet the supervisor before/after the tutorial, or any other time, as many times you need, subject to availability in his/her schedule.
Note that it is not the supervisor’s job to chase you down and give help. It is up to you to get as much feedback from them as you need. You are free to request more feedback from the supervisor as necessary. Similarly, it is not the job of the supervisor to lead your project to success.
What if I don’t carry around a laptop?
If you do not have a laptop or prefer not to bring the laptop, it is up to you to show your work to the tutor in some way (e.g. by connecting to your home PC remotely), without requiring extra time/effort from the tutor or team members.
Reason: As you enjoy the benefits of not bring the laptop; you (not others) should bear the cost too.
Outcomes
IDEs
W3.1 Can use basic features of an IDE
W3.1a Can explain IDEs
Implementation → IDEs →
What
Professional software engineers often write code using Integrated Development Environments (IDEs). IDEs support all development-related work within the same tool.
An IDE generally consists of:
- A source code editor that includes features such as syntax coloring, auto-completion, easy code navigation, error highlighting, and code-snippet generation.
- A compiler and/or an interpreter (together with other build automation support) that facilitates the compilation/linking/running/deployment of a program.
- A debugger that allows the developer to execute the program one step at a time to observe the run-time behavior in order to locate bugs.
- Other tools that aid various aspects of coding e.g. support for automated testing, drag-and-drop construction of UI components, version management support, simulation of the target runtime platform, and modeling support.
Examples of popular IDEs:
- Java: Eclipse, Intellij IDEA, NetBeans
- C#, C++: Visual Studio
- Swift: XCode
- Python: PyCharm
Some Web-based IDEs have appeared in recent times too e.g., Amazon's Cloud9 IDE.
Some experienced developers, in particular those with a UNIX background, prefer lightweight yet powerful text editors with scripting capabilities (e.g. Emacs) over heavier IDEs.
- a. Compiling
- b. Syntax error highlighting
- c. Debugging
- d. Code navigation e.g., to navigate from a method call to the method implementation
- e. Simulation e.g., run a mobile app in a simulator
- f. Code analysis e.g. to find unreachable code
- g. Reverse engineering design/documentation e.g. generate diagrams from code
- h. Visual programming e.g. Write programs using ‘drag and drop’ actions instead of typing code
- i. Syntax assistance e.g., show hints as you type
- j. Code generation e.g., to generate the code required by simply specifying which component/structure you want to implement
- k. Extension i.e., ability add more functionality to the IDE using plugins
All.
Explanation: While all of these features may not be present in some IDEs, most do have these features in some form or other.
Evidence:
Install Intellij IDEA on your computer. Either the Community Edition (free) or the Ultimate Edition (free for students) is fine.
W3.1b Can setup a project in an IDE
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Project Setup
Running Intellij IDEA for the First Time
A little bit more detailed explanation (from CodeLaunch) with some additional info at the end.
Importing a Project to Intellij IDEA
Evidence:
Acceptable: Any Java project set up in Intellij.
Suggested: Do the exercise given in AddressBook - Level1 : LO-IdeSetup
Submission: Demo the test during the tutorial.
W3.1c Can navigate code effectively using IDE features
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Code Navigation
Some useful navigation shortcuts:
- Quickly locate a file by name.
- Go to the definition of a method from where it is used.
- Go back to the previous location.
- View the documentation of a method from where the method is being used, without navigating to the method itself.
- Find where a method/field is being used.
Evidence:
Acceptable: Use Intellij basic code navigation features to navigate the code of any java project.
Suggested: Do the exercise given in AddressBook - Level1 : LO-CodeNavigation
Submission: Demo the test during the tutorial.
W3.2 Can use intermediate level features of an IDE
W3.2a Can explain debugging
Implementation → IDEs → Debugging →
What
Debugging is the process of discovering defects in the program. Here are some approaches to debugging:
-
Bad -- By inserting temporary print statements: This is an ad-hoc approach in which print statements are inserted in the program to print information relevant to debugging, such as variable values. e.g.
Exiting process() method, x is 5.347. This approach is not recommended due to these reasons.- Incurs extra effort when inserting and removing the print statements.
- Unnecessary program modifications increases the risk of introducing errors into the program.
- These print statements, if not promptly removed, may even appear unexpectedly in the production version.
-
Bad -- By manually tracing through the code: Otherwise known as ‘eye-balling’, this approach doesn't have the cons of the previous approach, but it too is not recommended (other than as a 'quick try') due to these reasons:
- It is difficult, time consuming, and error-prone technique.
- If you didn't spot the error while writing code, you might not spot the error when reading code too.
-
Good -- Using a debugger: A debugger tool allows you to pause the execution, then step through one statement at a time while examining the internal state if necessary. Most IDEs come with an inbuilt debugger. This is the recommended approach for debugging.
W3.2b Can step through a program using a debugger
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Debugging: Basic
This video (from LaunchCode) gives a pretty good explanation of how to use the Intellij IDEA debugger.
- Intellij IDEA Documentation: Debugging Basics - Can be used as a reference document when you want to recall how to use a debugging feature.
Evidence:
Submission: Demo debugging features of Intellij during the tutorial.
W3.2c Can use some useful IDE productivity shortcuts
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Productivity Shortcuts
Evidence:
Submission: Demo some Intellij productivity shortcuts during the tutorial.
Refactoring
W3.3 Can refactor code at a basic level
W3.3a Can explain refactoring
Implementation → Refactoring →
What
The first version of the code you write may not be of production quality. It is OK to first concentrate on making the code work, rather than worry over the quality of the code, as long as you improve the quality later. This process of improving a program's internal structure in small steps without modifying its external behavior is called refactoring.
- Refactoring is not rewriting: Discarding poorly-written code entirely and re-writing it from scratch is not refactoring because refactoring needs to be done in small steps.
- Refactoring is not bug fixing: By definition, refactoring is different from bug fixing or any other modifications that alter the external behavior (e.g. adding a feature) of the component in concern.
💡 Improving code structure can have many secondary benefits: e.g.
- hidden bugs become easier to spot
- improve performance (sometimes, simpler code runs faster than complex code because simpler code is easier for the compiler to optimize).
Given below are two common refactorings (
- Java: http://refactoring.com/catalog/ - This is a list of common refactorings, maintained by Martin Fowler, a leading authority on refactoring. He is also the author of the ‘bestseller’ on refactoring: Refactoring: Improving the Design of Existing Code
- Python: https://refactoring.guru/refactoring/catalog -- A catalog of refactorings applicable to Python code.
Refactoring Name: Consolidate Duplicate Conditional Fragments
Situation: The same fragment of code is in all branches of a conditional expression.
Method: Move it outside of the expression.
Example:
|
→ |
|
|
→ |
|
Refactoring Name: Extract Method
Situation: You have a code fragment that can be grouped together.
Method: Turn the fragment into a method whose name explains the purpose of the method.
Example:
void printOwing() {
printBanner();
//print details
System.out.println("name: " + name);
System.out.println("amount " + getOutstanding());
}
void printOwing() {
printBanner();
printDetails(getOutstanding());
}
void printDetails (double outstanding) {
System.out.println("name: " + name);
System.out.println("amount " + outstanding);
}
def print_owing():
print_banner()
//print details
print("name: " + name)
print("amount " + get_outstanding())
def print_owing():
print_banner()
print_details(get_outstanding())
def print_details(amount):
print("name: " + name)
print("amount " + amount)
💡 Some IDEs have built in support for basic refactorings such as automatically renaming a variable/method/class in all places it has been used.
Refactoring, even if done with the aid of an IDE, may still result in regressions. Therefore, each small refactoring should be followed by regression testing.
Choose the correct statements
- a. Refactoring can improve understandability
- b. Refactoring can uncover bugs
- c. Refactoring can result in better performance
- d. Refactoring can change the number of methods/classes
a, b, c, d
Explanation:
- (a, b, c) Although the primary aim of refactoring is to improve internal code structure, there are other secondary benefits.
- (d) Some refactorings result in adding/removing methods/classes.
Do you agree with the following statement? Justify your answer.
Statement: Whenever we refactor code to fix bugs, we need not do regression testing if the bug fix was minor.
There are two flaws in the given statement.
DISAGREE.
- Even a minor change can have major repercussions on the system. We MUST do regression testing after each change, no matter how minor it is.
- Fixing bugs is technically not refactoring.
Explain what is refactoring and why it is not the same as rewriting, bug fixing, or adding features.
Evidence:
Explain what is refactoring and why it is not the same as rewriting, bug fixing, or adding features.
W3.3b Can use automated refactoring features of the IDE
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Refactoring
This video explains how to automate the 'Extract parameter' refactoring using Intellij IDEA. Most other refactorings available works similarly. i.e. select the code to refactor → find the refactoring in the context menu or use the keyboard shortcut.
Here's another video explaining how to change a method signature as part of refactoring.
- Introduction to Refactoring (in Intellij IDEA) : An article on refactorings available in Intellij IDEA.
Evidence:
Acceptable: Ability to do some automated refactoring in the IDE.
Submission: Demo during the tutorial.
W3.3c Can apply some basic refactoring
Implementation → Refactoring →
How
Given below are some more commonly used refactorings. A more comprehensive list is available at
- Java: http://refactoring.com/catalog/ - This is a list of common refactorings, maintained by Martin Fowler, a leading authority on refactoring. He is also the author of the ‘bestseller’ on refactoring: Refactoring: Improving the Design of Existing Code
- Python: https://refactoring.guru/refactoring/catalog -- A catalog of refactorings applicable to Python code.
Evidence:
Acceptable: Some commits that show some refactorings (not necessarily the ones in the list above) you have done.
Suggested: Do some refactoring to the addressbook-level1 code. Remember to commit after each refactoring. The commit message should mention the refactoring you applied. e.g. AddressBook.java: extrace foo() method
Submission: Show the relevant commits during the tutorial.
W3.3d Can decide when to apply a given refactoring
Implementation → Refactoring →
When
We know that it is important to refactor frequently so as to avoid the accumulation of ‘messy’ code which might get out of control. But how much refactoring is too much refactoring? It is too much refactoring when the benefits no longer justify the cost. The costs and the benefits depend on the context. That is why some refactorings are ‘opposites’ of each other (e.g. extract method vs inline method).
‘Extract method’ and ‘Inline method’ refactorings
a
Evidence:
Give an example from any project (e.g. addressbook-level1) where a refactoring can be applied but you decide against it because it is not worth it.
Implementation
W3.4 C++ to Java
W3.4a Can explain what Java is
C++ to Java → The Java World →
What is Java?
Java was conceived by James Gosling and his team at Sun Microsystems in 1991.
Java is directly related to both C and C++. Java inherits its syntax from C. Its object model is adapted from C++. --Java: A Beginner’s Guide, by Oracle
Fun fact: The language was initially called Oak after an oak tree that stood outside Gosling's office. Later the project went by the name Green and was finally renamed Java, from Java coffee. --Wikipedia
Oracle became the owner of Java in 2010, when it acquired Sun Microsystems.
Java has remained the most popular language in the world for several years now (as at July 2018), according to the TIOBE index.
W3.4b Can explain how Java works at a higher-level
C++ to Java → The Java World →
How Java Works
Java is both
Java technology is both a programming language and a platform. The Java programming language is a high-level object-oriented language that has a particular syntax and style. A Java platform is a particular environment in which Java programming language applications run. --Oracle
W3.4c Can explain Java editions
C++ to Java → The Java World →
Java Editions
According to the Official Java documentation, there are four platforms of the Java programming language:
-
Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE): Contains the core functionality of the Java programming language.
-
Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE): For developing and running large-scale enterprise applications. Built on top of Java SE.
-
Java Platform, Micro Edition (Java ME): For Java programming language applications meant for small devices, like mobile phones. A subset of Java SE.
-
JavaFX: For creating applications with graphical user interfaces. Can work with the other three above.
This book chapter uses the Java SE edition unless stated otherwise.
W3.5 Can implement classes
W3.5a Can define Java classes
:
C++ to Java → Classes →
Defining Classes
As you know,
- Defining a class creates a new object type with the same name.
- Every object belongs to some object type; that is, it is an instance of some class.
- A class definition is like a template for objects: it specifies what attributes the objects have and what methods can operate on them.
- The
newoperator instantiates objects, that is, it creates new instances of a class. - The methods that operate on an object type are defined in the class for that object.
Here's a class called Time, intended to represent a moment in time. It has three attributes and no methods.
public class Time {
private int hour;
private int minute;
private int second;
}
You can give a class any name you like. The Java convention is to use
The code should be in a file whose name matches the class e.g., the Time class should be in a file named Time.java.
When a class is public (e.g., the Time class in the above example) it can be used in other classes. But the
private (e.g., the hour, minute and second attributes of the Time class) can only be accessed from inside the Time class.
Constructos
The syntax for
- The name of the constructor is the same as the name of the class.
- The keyword
staticis omitted. - Do not return anything. A constructor returns the created object by default.
When you invoke new, Java creates the object and calls your constructor to initialize the instance variables. When the constructor is done, new returns a reference to the new object.
Here is an example constructor for the Time class:
public Time() {
hour = 0;
minute = 0;
second = 0;
}
This constructor does not take any arguments. Each line initializes an instance variable to zero (which in this example means midnight). Now you can create Time objects.
Time time = new Time();
Like other methods, constructors can be overloaded, which means you can provide multiple constructors with different parameters.
You can add another constructor to the Time class to allow creating Time objects that are initialized to a specific time:
public Time(int h, int m, int s) {
hour = h;
minute = m;
second = s;
}
Here's how you can invoke the new constructor:
Time justBeforeMidnight = new Time(11, 59, 59);
this keyword
The this keyword is a reference variable in Java that refers to the current object. You can use this the same way you use the name of any other object. For example, you can read and write
the instance variables of this, and you can pass this as an argument to other methods. But you do not declare this, and you can’t make an assignment to it.
In the following version of the constructor, the names and types of the parameters are the same as the instance variables (parameters don’t have to use the same names, but that’s a common style).
As a result, the parameters shadow (or hide) the instance variables, so the keyword this is necessary to tell them apart.
public Time(int hour, int minute, int second) {
this.hour = hour;
this.minute = minute;
this.second = second;
}
this can be used to refer to a constructor of a class within the same class too.
In this example the constructor Time() uses the this keyword to call its own overloaded constructor Time(int, int, int)
public Time() {
this(0, 0, 0); // call the overloaded constructor
}
public Time(int hour, int minute, int second) {
// ...
}
Instance methods
You can add methods to a class which can then be used from the objects of that class. These instance methods do not have the static keyword in the method signature. Instance methods can access
attributes of the class.
Here's how you can add a method to the Time class to get the number of seconds passed till midnight.
public int secondsSinceMidnight() {
return hour*60*60 + minute*60 + second;
}
Here's how you can use that method.
Time t = new Time(0, 2, 5);
System.out.println(t.secondsSinceMidnight() + " seconds since midnight!");
Define a Circle class so that the code given below produces the given output. The nature of the class is a follows:
- Attributes(all
private):int x,int y: represents the location of the circledouble radius: the radius of the circle
- Constructors:
Circle(): initializesx,y,radiusto 0Circle(int x, int y, double radius): initializes the attributes to the given values
- Methods:
getArea():int
Returns the area of the circle as anintvalue (notdouble). Calculated as 2xPIx(radius)2
💡 You can convert todoubleto anintusing(int)e.g.,x = (int)2.25givesxthe value2.
💡 You can useMath.PIto get the value of Pi
💡 You can useMath.pow()to raise a number to a specific power e.g.,Math.pow(3, 2)calculates 32
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle c = new Circle();
System.out.println(c.getArea());
c = new Circle(1, 2, 5);
System.out.println(c.getArea());
}
}
0
78
- Put the
Circleclass in a file calledCircle.java
Partial solution:
public class Circle {
private int x;
// ...
public Circle(){
this(0, 0, 0);
}
public Circle(int x, int y, double radius){
this.x = x;
// ...
}
public int getArea(){
double area = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
return (int)area;
}
}
W3.5b Can define getters and setters
:
C++ to Java → Classes →
Getters and setters
As the instance variables of Time are private, you can access them from within the Time class only. To compensate, you can provide methods to access attributes:
public int getHour() {
return hour;
}
public int getMinute() {
return minute;
}
public int getSecond() {
return second;
}
Methods like these are formally called “accessors”, but more commonly referred to as getters. By convention, the method that gets a variable named something is called getSomething.
Similarly, you can provide setter methods to modify attributes of a Time object:
public void setHour(int hour) {
this.hour = hour;
}
public void setMinute(int minute) {
this.minute = minute;
}
public void setSecond(int second) {
this.second = second;
}
Consider the Circle class below:
public class Circle {
private int x;
private int y;
private double radius;
public Circle(){
this(0, 0, 0);
}
public Circle(int x, int y, double radius){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}
public int getArea(){
double area = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
return (int)area;
}
}
Update it as follows so that code given below produces the given output.
- Add getter/setter methods for all three attributes
- Update the setters and constructors such that if the radius supplied is negative, the code automatically set the radius to 0 instead.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle c = new Circle(1,2, 5);
c.setX(4);
c.setY(5);
c.setRadius(6);
System.out.println("x : " + c.getX());
System.out.println("y : " + c.getY());
System.out.println("radius : " + c.getRadius());
System.out.println("area : " + c.getArea());
c.setRadius(-5);
System.out.println("radius : " + c.getRadius());
c = new Circle(1, 1, -4);
System.out.println("radius : " + c.getRadius());
}
}
x : 4
y : 5
radius : 6.0
area : 113
radius : 0.0
radius : 0.0
Partial solution:
public Circle(int x, int y, double radius){
setX(x);
setY(y);
setRadius(radius);
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = Math.max(radius, 0);
}
W3.6 Can implement class-level members
W3.6a Can explain class-level members
Paradigms → Object Oriented Programming → Classes →
Class-Level Members
While all objects of a class has the same attributes, each object has its own copy of the attribute value.
All Person objects have the Name attribute but the value of that attribute varies between Person objects.
However, some attributes are not suitable to be maintained by individual objects. Instead, they should be maintained centrally, shared by all objects of the class. They are like ‘global variables’ but attached to a specific class. Such variables whose value is shared by all instances of a class are called class-level attributes.
The attribute totalPersons should be maintained centrally and shared by all Person objects rather than copied at each Person object.
Similarly, when a normal method is being called, a message is being sent to the receiving object and the result may depend on the receiving object.
Sending the getName() message to Adam object results in the response "Adam" while sending the same message to the Beth object gets
the response "Beth".
However, there can be methods related to a specific class but not suitable for sending message to a specific object of that class. Such methods that are called using the class instead of a specific instance are called class-level methods.
The method getTotalPersons() is not suitable to send to a specific Person object because a specific object of the Person class should not know about the total number of Person objects.
Class-level attributes and methods are collectively called class-level members (also called static members sometimes because some programming languages use the keyword static to identify class-level members). They are to be accessed using the class name rather than an instance of the class.
Which of these are suitable as class-level variables?
- a. system: multi-player Pac Man game, Class:
Player, variable:totalScore - b. system: eLearning system, class:
Course, variable:totalStudents - c. system: ToDo manager, class:
Task, variable:totalPendingTasks - d. system: any, class:
ArrayList, variable:total(i.e., total items in a givenArrayListobject)
(c)
Explanation: totalPendingTasks should not be managed by individual Task objects and therefore suitable to be maintained as a class-level variable. The other variables should be managed at instance
level as their value varies from instance to instance. e.g., totalStudents for one Course object will differ from totalStudents of another.
W3.7 Can use Java varargs feature
W3.7a Can use Java varargs feature
Tools → Java →
Varargs
Evidence:
Acceptable: Some code that you have written that uses the varargs feature.
Suggested: Do the exercise given in AddressBook - Level1 : LO-Varargs
Submission: Show your code to the tutor during the tutorial.
🅿️ Project
W3.8 Can define the target of a product
Covered by:
W3.9 Can work with a 1KLoC code base
This LO can earn you
10 marks allocated for participation can be earned in the following ways (there are ~28 available marks to choose from):
-
Good peer ratings - Criteria for professional conduct (1 mark for each criterion, max 7)
- Competency criteria (2 marks for each, max 6)
- In-lecture quizzes
- In-lecture quizzes, roughly two questions each week (0.5 each, max 10 marks)
- Module admin tasks done on time and as instructed
- Peer evaluations (1 mark each)
- Pre-module survey (1 mark)
- Enhanced AB1-AB3: 2 mark each
Relevant: [
Peer evaluation criteria: professional conduct
- Professional Communication :
- Communicates sufficiently and professionally. e.g. Does not use offensive language or excessive slang in project communications.
- Responds to communication from team members in a timely manner (e.g. within 24 hours).
- Punctuality: Does not cause others to waste time or slow down project progress by frequent tardiness.
- Dependability: Promises what can be done, and delivers what was promised.
- Effort: Puts in sufficient effort to, and tries their best to keep up with the module/project pace. Seeks help from others when necessary.
- Quality: Does not deliver work products that seem to be below the student's competence level i.e. tries their best to make the work product as high quality as possible within her competency level.
- Meticulousness:
- Rarely overlooks submission requirements.
- Rarely misses compulsory module activities such as completing the TEAMMATES profile or peer review.
- Teamwork: How willing are you to act as part of a team, contribute to team-level tasks, adhere to team decisions, etc.
Peer evaluation criteria: competency
- Technical Competency: Able to gain competency in all the required tools and techniques.
- Mentoring skills: Helps others when possible. Able to mentor others well.
- Communication skills: Able to communicate (written and spoken) well. Takes initiative in discussions.
Evidence:
Do an enhancement to [AddressBook - Level1] e.g. add a new command
-
The size of the enhancement does not matter.
-
Step 1: Fork address AddressBook - Level1 to your GitHub account.
-
Step 2: Change the code in small steps and commit after each significant change. You may commit to the
masterbranch.- Try to stay within the procedural (not OOP) style of the code base. Reason: in this LO, we try to stretch ourselves to the limits of the procedural approach.
- Update all relevant tests. Ensure all tests pass.
- [Optional] Update all relevant documentation.
- [Optional/Recommended] Try to follow our coding standard in your new code.
-
Step 3: push the updated AB1 code to your fork
Note that you can reuse the code you write here in your final project, if applicable.
Submission: No special submission required. Our scripts will check your fork automatically.
Tutorial 3
CS2113 students only: Form teams at the beginning of the tutorial. Be sure to conform to team forming constrains.
All students:
- Confirm your team ID with the tutor. It should be of the form
TUTORIAL_ID-TEAM_NUMBERe.g.W12-2(Wed1200 slot, team2) - Create an organization on GitHub using your team ID.
- As before, discuss evidence of achieving LOs as directed by the tutor.
Suggested activity to do in the tutorial:
Suppose we wrote a program to follow the class structure given in this class diagram:
Draw object diagrams to represent the object structures after each of these steps below. Assume that we are trying to minimize the number of total objects.
i.e. apply step 1 → [diagram 1] → apply step 2 on diagram 1 → [diagram 2] and so on.
-
There are no persons.
-
Alfredis the Guardian ofBruce. -
Bruce's contact number is the same asAlfred's. -
Alfredis also the guardian of another person. That person listsAlfreds home address as his home address as well as office address. -
Alfredhas a an office address atWayne Industriesbuilding which is different from his home address (i.e.Bat Cave).
After step 2, the diagram should be like this:
- Write code to implement the classes given in the class diagram
W3.1a Can explain IDEs
Implementation → IDEs →
What
Professional software engineers often write code using Integrated Development Environments (IDEs). IDEs support all development-related work within the same tool.
An IDE generally consists of:
- A source code editor that includes features such as syntax coloring, auto-completion, easy code navigation, error highlighting, and code-snippet generation.
- A compiler and/or an interpreter (together with other build automation support) that facilitates the compilation/linking/running/deployment of a program.
- A debugger that allows the developer to execute the program one step at a time to observe the run-time behavior in order to locate bugs.
- Other tools that aid various aspects of coding e.g. support for automated testing, drag-and-drop construction of UI components, version management support, simulation of the target runtime platform, and modeling support.
Examples of popular IDEs:
- Java: Eclipse, Intellij IDEA, NetBeans
- C#, C++: Visual Studio
- Swift: XCode
- Python: PyCharm
Some Web-based IDEs have appeared in recent times too e.g., Amazon's Cloud9 IDE.
Some experienced developers, in particular those with a UNIX background, prefer lightweight yet powerful text editors with scripting capabilities (e.g. Emacs) over heavier IDEs.
- a. Compiling
- b. Syntax error highlighting
- c. Debugging
- d. Code navigation e.g., to navigate from a method call to the method implementation
- e. Simulation e.g., run a mobile app in a simulator
- f. Code analysis e.g. to find unreachable code
- g. Reverse engineering design/documentation e.g. generate diagrams from code
- h. Visual programming e.g. Write programs using ‘drag and drop’ actions instead of typing code
- i. Syntax assistance e.g., show hints as you type
- j. Code generation e.g., to generate the code required by simply specifying which component/structure you want to implement
- k. Extension i.e., ability add more functionality to the IDE using plugins
All.
Explanation: While all of these features may not be present in some IDEs, most do have these features in some form or other.
Evidence:
Install Intellij IDEA on your computer. Either the Community Edition (free) or the Ultimate Edition (free for students) is fine.
W3.1b Can setup a project in an IDE
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Project Setup
Running Intellij IDEA for the First Time
A little bit more detailed explanation (from CodeLaunch) with some additional info at the end.
Importing a Project to Intellij IDEA
Evidence:
Acceptable: Any Java project set up in Intellij.
Suggested: Do the exercise given in AddressBook - Level1 : LO-IdeSetup
Submission: Demo the test during the tutorial.
W3.1c Can navigate code effectively using IDE features
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Code Navigation
Some useful navigation shortcuts:
- Quickly locate a file by name.
- Go to the definition of a method from where it is used.
- Go back to the previous location.
- View the documentation of a method from where the method is being used, without navigating to the method itself.
- Find where a method/field is being used.
Evidence:
Acceptable: Use Intellij basic code navigation features to navigate the code of any java project.
Suggested: Do the exercise given in AddressBook - Level1 : LO-CodeNavigation
Submission: Demo the test during the tutorial.
W3.2b Can step through a program using a debugger
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Debugging: Basic
This video (from LaunchCode) gives a pretty good explanation of how to use the Intellij IDEA debugger.
- Intellij IDEA Documentation: Debugging Basics - Can be used as a reference document when you want to recall how to use a debugging feature.
Evidence:
Submission: Demo debugging features of Intellij during the tutorial.
W3.2c Can use some useful IDE productivity shortcuts
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Productivity Shortcuts
Evidence:
Submission: Demo some Intellij productivity shortcuts during the tutorial.
W3.3a Can explain refactoring
Implementation → Refactoring →
What
The first version of the code you write may not be of production quality. It is OK to first concentrate on making the code work, rather than worry over the quality of the code, as long as you improve the quality later. This process of improving a program's internal structure in small steps without modifying its external behavior is called refactoring.
- Refactoring is not rewriting: Discarding poorly-written code entirely and re-writing it from scratch is not refactoring because refactoring needs to be done in small steps.
- Refactoring is not bug fixing: By definition, refactoring is different from bug fixing or any other modifications that alter the external behavior (e.g. adding a feature) of the component in concern.
💡 Improving code structure can have many secondary benefits: e.g.
- hidden bugs become easier to spot
- improve performance (sometimes, simpler code runs faster than complex code because simpler code is easier for the compiler to optimize).
Given below are two common refactorings (
- Java: http://refactoring.com/catalog/ - This is a list of common refactorings, maintained by Martin Fowler, a leading authority on refactoring. He is also the author of the ‘bestseller’ on refactoring: Refactoring: Improving the Design of Existing Code
- Python: https://refactoring.guru/refactoring/catalog -- A catalog of refactorings applicable to Python code.
Refactoring Name: Consolidate Duplicate Conditional Fragments
Situation: The same fragment of code is in all branches of a conditional expression.
Method: Move it outside of the expression.
Example:
|
→ |
|
|
→ |
|
Refactoring Name: Extract Method
Situation: You have a code fragment that can be grouped together.
Method: Turn the fragment into a method whose name explains the purpose of the method.
Example:
void printOwing() {
printBanner();
//print details
System.out.println("name: " + name);
System.out.println("amount " + getOutstanding());
}
void printOwing() {
printBanner();
printDetails(getOutstanding());
}
void printDetails (double outstanding) {
System.out.println("name: " + name);
System.out.println("amount " + outstanding);
}
def print_owing():
print_banner()
//print details
print("name: " + name)
print("amount " + get_outstanding())
def print_owing():
print_banner()
print_details(get_outstanding())
def print_details(amount):
print("name: " + name)
print("amount " + amount)
💡 Some IDEs have built in support for basic refactorings such as automatically renaming a variable/method/class in all places it has been used.
Refactoring, even if done with the aid of an IDE, may still result in regressions. Therefore, each small refactoring should be followed by regression testing.
Choose the correct statements
- a. Refactoring can improve understandability
- b. Refactoring can uncover bugs
- c. Refactoring can result in better performance
- d. Refactoring can change the number of methods/classes
a, b, c, d
Explanation:
- (a, b, c) Although the primary aim of refactoring is to improve internal code structure, there are other secondary benefits.
- (d) Some refactorings result in adding/removing methods/classes.
Do you agree with the following statement? Justify your answer.
Statement: Whenever we refactor code to fix bugs, we need not do regression testing if the bug fix was minor.
There are two flaws in the given statement.
DISAGREE.
- Even a minor change can have major repercussions on the system. We MUST do regression testing after each change, no matter how minor it is.
- Fixing bugs is technically not refactoring.
Explain what is refactoring and why it is not the same as rewriting, bug fixing, or adding features.
Evidence:
Explain what is refactoring and why it is not the same as rewriting, bug fixing, or adding features.
W3.3b Can use automated refactoring features of
the IDE
Tools → Intellij IDEA →
Refactoring
This video explains how to automate the 'Extract parameter' refactoring using Intellij IDEA. Most other refactorings available works similarly. i.e. select the code to refactor → find the refactoring in the context menu or use the keyboard shortcut.
Here's another video explaining how to change a method signature as part of refactoring.
- Introduction to Refactoring (in Intellij IDEA) : An article on refactorings available in Intellij IDEA.
Evidence:
Acceptable: Ability to do some automated refactoring in the IDE.
Submission: Demo during the tutorial.
W3.3c Can apply some basic refactoring
Implementation → Refactoring →
How
Given below are some more commonly used refactorings. A more comprehensive list is available at
- Java: http://refactoring.com/catalog/ - This is a list of common refactorings, maintained by Martin Fowler, a leading authority on refactoring. He is also the author of the ‘bestseller’ on refactoring: Refactoring: Improving the Design of Existing Code
- Python: https://refactoring.guru/refactoring/catalog -- A catalog of refactorings applicable to Python code.
Evidence:
Acceptable: Some commits that show some refactorings (not necessarily the ones in the list above) you have done.
Suggested: Do some refactoring to the addressbook-level1 code. Remember to commit after each refactoring. The commit message should mention the refactoring you applied. e.g. AddressBook.java: extrace foo() method
Submission: Show the relevant commits during the tutorial.
W3.3d Can decide when to apply a given refactoring
Implementation → Refactoring →
When
We know that it is important to refactor frequently so as to avoid the accumulation of ‘messy’ code which might get out of control. But how much refactoring is too much refactoring? It is too much refactoring when the benefits no longer justify the cost. The costs and the benefits depend on the context. That is why some refactorings are ‘opposites’ of each other (e.g. extract method vs inline method).
‘Extract method’ and ‘Inline method’ refactorings
a
Evidence:
Give an example from any project (e.g. addressbook-level1) where a refactoring can be applied but you decide against it because it is not worth it.
W3.7a Can use Java varargs feature
Tools → Java →
Varargs
Evidence:
Acceptable: Some code that you have written that uses the varargs feature.
Suggested: Do the exercise given in AddressBook - Level1 : LO-Varargs
Submission: Show your code to the tutor during the tutorial.
W3.8 Can define the target of a product
Covered by:
W3.9 Can work with a 1KLoC code base
This LO can earn you
10 marks allocated for participation can be earned in the following ways (there are ~28 available marks to choose from):
-
Good peer ratings - Criteria for professional conduct (1 mark for each criterion, max 7)
- Competency criteria (2 marks for each, max 6)
- In-lecture quizzes
- In-lecture quizzes, roughly two questions each week (0.5 each, max 10 marks)
- Module admin tasks done on time and as instructed
- Peer evaluations (1 mark each)
- Pre-module survey (1 mark)
- Enhanced AB1-AB3: 2 mark each
Relevant: [
Peer evaluation criteria: professional conduct
- Professional Communication :
- Communicates sufficiently and professionally. e.g. Does not use offensive language or excessive slang in project communications.
- Responds to communication from team members in a timely manner (e.g. within 24 hours).
- Punctuality: Does not cause others to waste time or slow down project progress by frequent tardiness.
- Dependability: Promises what can be done, and delivers what was promised.
- Effort: Puts in sufficient effort to, and tries their best to keep up with the module/project pace. Seeks help from others when necessary.
- Quality: Does not deliver work products that seem to be below the student's competence level i.e. tries their best to make the work product as high quality as possible within her competency level.
- Meticulousness:
- Rarely overlooks submission requirements.
- Rarely misses compulsory module activities such as completing the TEAMMATES profile or peer review.
- Teamwork: How willing are you to act as part of a team, contribute to team-level tasks, adhere to team decisions, etc.
Peer evaluation criteria: competency
- Technical Competency: Able to gain competency in all the required tools and techniques.
- Mentoring skills: Helps others when possible. Able to mentor others well.
- Communication skills: Able to communicate (written and spoken) well. Takes initiative in discussions.
Evidence:
Do an enhancement to [AddressBook - Level1] e.g. add a new command
-
The size of the enhancement does not matter.
-
Step 1: Fork address AddressBook - Level1 to your GitHub account.
-
Step 2: Change the code in small steps and commit after each significant change. You may commit to the
masterbranch.- Try to stay within the procedural (not OOP) style of the code base. Reason: in this LO, we try to stretch ourselves to the limits of the procedural approach.
- Update all relevant tests. Ensure all tests pass.
- [Optional] Update all relevant documentation.
- [Optional/Recommended] Try to follow our coding standard in your new code.
-
Step 3: push the updated AB1 code to your fork
Note that you can reuse the code you write here in your final project, if applicable.
Submission: No special submission required. Our scripts will check your fork automatically.
Lecture 3
Slides: Uploaded on IVLE.